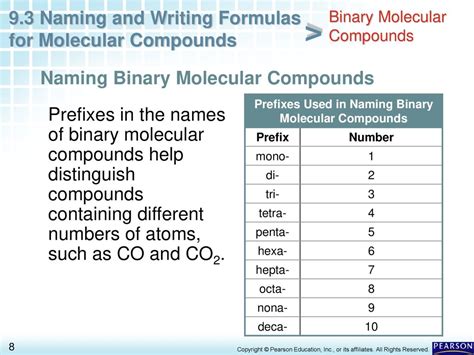
The chemical compound dinitrogen trioxide, also known as nitrogen trioxide or N2O3, is a molecule composed of two nitrogen atoms and three oxygen atoms. This compound is of significant interest in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and environmental science, due to its unique properties and reactivity. In this article, we will delve into the details of dinitrogen trioxide, exploring its structure, synthesis, properties, and applications, as well as its role in atmospheric chemistry and environmental processes.
Key Points
- Dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3) is a nitrogen oxide compound with significant implications in atmospheric chemistry and environmental science.
- The compound exhibits unique chemical properties, including its ability to act as an oxidizing agent and its role in the formation of acid rain.
- N2O3 is synthesized through the reaction of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO) under specific conditions.
- The compound plays a crucial role in the Earth's atmosphere, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and particulate matter.
- Understanding the chemistry and environmental impact of dinitrogen trioxide is essential for developing strategies to mitigate air pollution and protect public health.
Chemical Structure and Synthesis
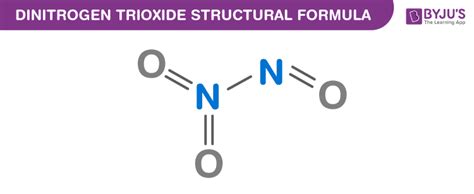
Dinitrogen trioxide is a covalently bonded molecule, consisting of a central nitrogen atom bonded to another nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms. The molecule can be synthesized through the reaction of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO) in the presence of a catalyst, such as ozone (O3) or ultraviolet light. This reaction is highly dependent on the conditions, including temperature, pressure, and the presence of other reactants.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Dinitrogen trioxide exhibits several distinct physical and chemical properties, including its deep blue color, high reactivity, and ability to act as an oxidizing agent. The compound is highly soluble in water, forming nitric acid (HNO3) and nitrous acid (HNO2), which are key components of acid rain. N2O3 is also a strong oxidizer, capable of reacting with a wide range of substances, including organic compounds and metals.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 76.01 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 3.5 °C |
| Melting Point | -100.8 °C |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble |

Environmental Impact and Applications
Dinitrogen trioxide plays a significant role in the Earth’s atmosphere, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone (O3) and particulate matter (PM). The compound is also a key component of acid rain, which can have devastating effects on ecosystems and infrastructure. Despite its negative environmental impacts, N2O3 has several industrial applications, including the production of nitric acid, fertilizers, and pharmaceuticals.
Atmospheric Chemistry and Environmental Processes
The chemistry of dinitrogen trioxide is closely linked to atmospheric processes, including the formation of ozone and particulate matter. N2O3 can react with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other atmospheric pollutants, leading to the formation of ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter. These pollutants can have significant negative impacts on public health, including respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease.
What is the primary source of dinitrogen trioxide in the atmosphere?
+The primary source of dinitrogen trioxide in the atmosphere is the reaction of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO) in the presence of a catalyst, such as ozone (O3) or ultraviolet light.
What are the negative environmental impacts of dinitrogen trioxide?
+Dinitrogen trioxide contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone and particulate matter, which can have devastating effects on ecosystems and infrastructure. The compound is also a key component of acid rain, which can harm aquatic life and damage buildings and monuments.
What are the industrial applications of dinitrogen trioxide?
+Dinitrogen trioxide is used in the production of nitric acid, fertilizers, and pharmaceuticals. The compound is also used as an oxidizing agent in various industrial processes.
In conclusion, dinitrogen trioxide is a complex and multifaceted compound with significant implications in atmospheric chemistry and environmental science. Understanding the chemistry and reactivity of N2O3 is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate air pollution and protect public health. By exploring the properties, synthesis, and applications of dinitrogen trioxide, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between chemical compounds and the environment.