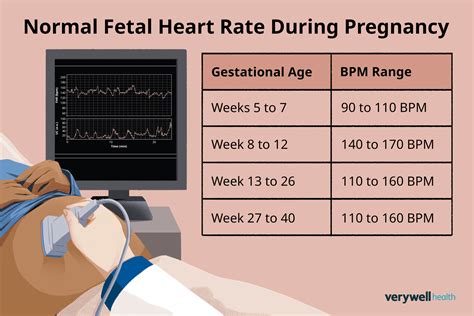
The normal fetal heart rate (FHR) is a crucial indicator of fetal well-being during pregnancy. A normal FHR typically ranges from 110 to 160 beats per minute (bpm), with an average rate of around 140 bpm. This range can vary slightly depending on the gestational age and the individual fetus. It's essential to monitor FHR regularly during pregnancy to detect any potential abnormalities or signs of fetal distress.
Fetal heart rate monitoring is typically performed using cardiotocography (CTG), which involves attaching sensors to the mother's abdomen to measure the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions. This non-invasive test provides valuable information about fetal well-being and can help identify potential complications early on. In addition to CTG, other methods such as Doppler ultrasound and fetal echocardiography can also be used to assess fetal heart rate and cardiac function.
Key Points
- The normal fetal heart rate ranges from 110 to 160 beats per minute (bpm), with an average rate of around 140 bpm.
- Fetal heart rate monitoring is crucial for detecting potential abnormalities or signs of fetal distress.
- Cardiotocography (CTG) is a common method used to monitor fetal heart rate and uterine contractions.
- Other methods, such as Doppler ultrasound and fetal echocardiography, can also be used to assess fetal heart rate and cardiac function.
- Monitoring fetal heart rate regularly during pregnancy can help identify potential complications early on.
Factors Affecting Fetal Heart Rate
Several factors can influence fetal heart rate, including gestational age, fetal movement, and maternal factors such as hydration and oxygenation. For example, fetal heart rate can increase during periods of fetal activity or decrease during periods of fetal sleep. Maternal factors, such as dehydration or hypoxia, can also impact fetal heart rate and overall fetal well-being.
It's also important to note that fetal heart rate can vary slightly from one pregnancy to another, and what is considered a normal range for one fetus may not be the same for another. Therefore, it's essential to work with a healthcare provider to establish a baseline fetal heart rate and monitor any changes or abnormalities throughout pregnancy.
Gestational Age and Fetal Heart Rate
Fetal heart rate can vary depending on gestational age. During early pregnancy, the fetal heart rate is typically faster, ranging from 160 to 200 bpm. As the pregnancy progresses, the fetal heart rate slows down, reaching a range of 110 to 160 bpm by around 20 weeks gestation. Understanding these changes is crucial for accurate fetal heart rate monitoring and interpretation.
| Gestational Age | Fetal Heart Rate Range |
|---|---|
| Early pregnancy (6-8 weeks) | 160-200 bpm |
| Mid-pregnancy (12-18 weeks) | 140-160 bpm |
| Late pregnancy (20-40 weeks) | 110-160 bpm |

Abnormal Fetal Heart Rate Patterns
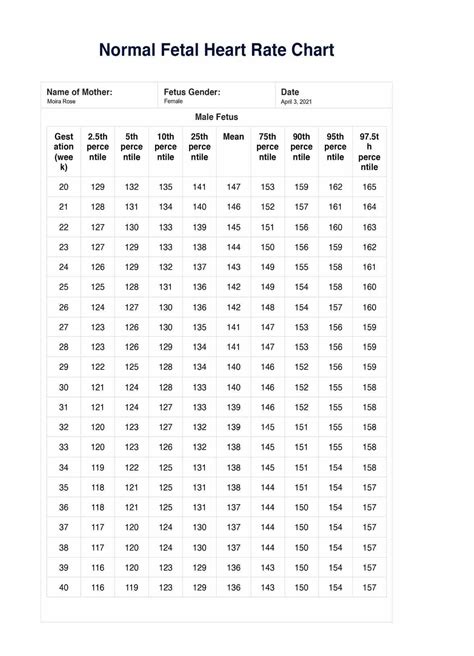
Abnormal fetal heart rate patterns can indicate potential complications or fetal distress. Some common abnormal patterns include bradycardia (a heart rate below 110 bpm), tachycardia (a heart rate above 160 bpm), and variable decelerations. These patterns can be detected through cardiotocography (CTG) or other fetal heart rate monitoring methods.
In cases where abnormal fetal heart rate patterns are detected, further evaluation and testing may be necessary to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. This may involve additional fetal monitoring, ultrasound examinations, or other diagnostic tests to assess fetal well-being and guide clinical decision-making.
Bradycardia and Fetal Distress
Bradycardia, or a fetal heart rate below 110 bpm, can be a sign of fetal distress. This condition can occur due to various factors, including maternal hypoxia, umbilical cord compression, or fetal hypoxia. In cases of bradycardia, prompt medical attention is essential to prevent potential complications and ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
Other abnormal fetal heart rate patterns, such as tachycardia or variable decelerations, can also indicate fetal distress or other complications. A comprehensive understanding of these patterns and their underlying causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
What is a normal fetal heart rate range?
+A normal fetal heart rate range is typically between 110 and 160 beats per minute (bpm), with an average rate of around 140 bpm.
How is fetal heart rate monitored during pregnancy?
+Fetal heart rate is typically monitored using cardiotocography (CTG), which involves attaching sensors to the mother’s abdomen to measure the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions.
What factors can influence fetal heart rate?
+Several factors can influence fetal heart rate, including gestational age, fetal movement, and maternal factors such as hydration and oxygenation.