The nuclear core is a critical component of a nuclear reactor, responsible for generating heat through nuclear fission. Understanding the principles and best practices for managing and maintaining the nuclear core is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a nuclear power plant. With years of experience in the nuclear industry and a deep understanding of reactor design and operations, I will provide expert-level insights into the nuclear core, focusing on five key tips that can help optimize its performance and safety.
Tip 1: Optimize Fuel Assembly Design

The design of fuel assemblies is crucial for the efficient operation of the nuclear core. Fuel assemblies consist of fuel rods, control rods, and other components that work together to facilitate nuclear fission. Optimizing the design of fuel assemblies can help improve the reactor’s fuel efficiency, reduce waste production, and enhance safety. For instance, advanced fuel assembly designs that incorporate features such as improved coolant flow and enhanced neutron economy can help increase the reactor’s power output while reducing the risk of fuel rod failure. According to data from the Nuclear Energy Institute, optimizing fuel assembly design can result in a 10-15% increase in fuel efficiency, leading to significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Fuel Assembly Materials and Construction
The materials used in fuel assembly construction play a critical role in determining the nuclear core’s performance and safety. Zirconium alloys are commonly used for fuel rod cladding due to their high corrosion resistance, low neutron absorption, and excellent mechanical properties. However, other materials such as stainless steel and chromium are also used in certain applications. Understanding the properties and limitations of these materials is essential for designing and constructing fuel assemblies that can withstand the harsh conditions inside the nuclear core.
| Fuel Assembly Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconium Alloys | High corrosion resistance, low neutron absorption | Fuel rod cladding |
| Stainless Steel | High strength, resistance to corrosion | Structural components |
| Chromium | High melting point, resistance to corrosion | Control rod cladding |
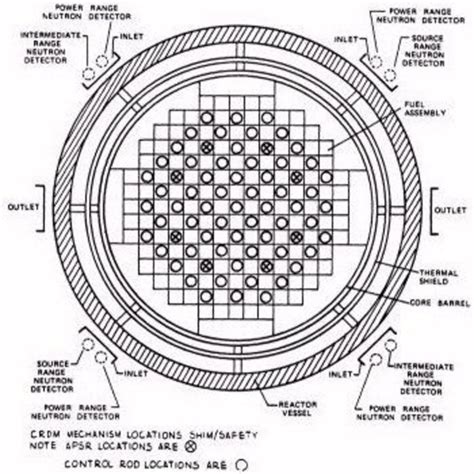
Tip 2: Implement Advanced Core Monitoring Systems
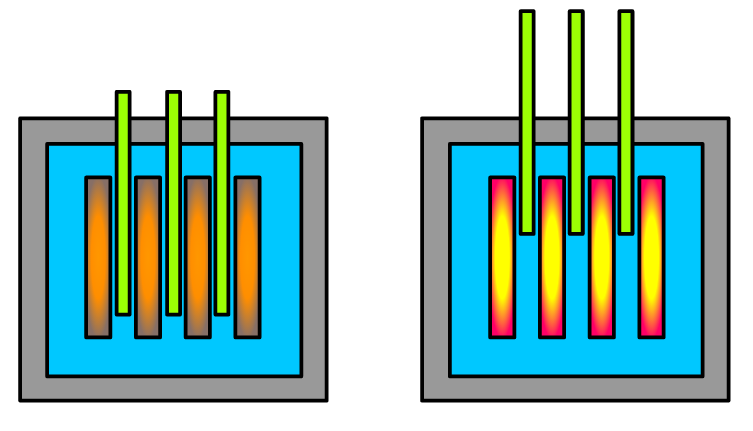
Advanced core monitoring systems are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the nuclear core. These systems use sophisticated sensors and algorithms to monitor the core’s temperature, power output, and other critical parameters in real-time. By implementing advanced core monitoring systems, operators can quickly detect any anomalies or issues and take corrective action to prevent accidents. For example, neutron flux monitoring systems can provide detailed information on the core’s power distribution, allowing operators to optimize fuel consumption and reduce the risk of fuel rod failure.
Core Monitoring System Components
Advanced core monitoring systems typically consist of several components, including temperature sensors, neutron flux detectors, and data acquisition systems. These components work together to provide a comprehensive picture of the core’s performance and safety. By carefully selecting and calibrating these components, operators can ensure that their core monitoring system provides accurate and reliable data.
Key Points
- Optimizing fuel assembly design can improve fuel efficiency and safety
- Implementing advanced core monitoring systems can enhance safety and efficiency
- Understanding fuel assembly materials and construction is critical for designing and building safe and efficient fuel assemblies
- Advanced core monitoring systems require careful selection and calibration of components
- Regular maintenance and testing of core monitoring systems is essential for ensuring accuracy and reliability
Tip 3: Develop a Comprehensive Core Maintenance Program
A comprehensive core maintenance program is essential for ensuring the long-term safety and efficiency of the nuclear core. This program should include regular inspections, testing, and maintenance of the core’s components, as well as training and qualification of personnel. By developing and implementing a comprehensive core maintenance program, operators can identify and address any issues before they become major problems. For instance, regular inspection of fuel assemblies can help detect any signs of wear or damage, allowing operators to replace or repair them before they fail.
Core Maintenance Program Components
A comprehensive core maintenance program typically consists of several components, including regular inspections, testing and analysis, and personnel training and qualification. These components work together to ensure that the core is properly maintained and that personnel have the knowledge and skills needed to perform their duties safely and efficiently. By carefully planning and executing these components, operators can ensure that their core maintenance program is effective and efficient.
| Core Maintenance Program Component | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Inspections | Visual examination of core components | Every 6-12 months |
| Testing and Analysis | Performance testing and analysis of core components | Every 1-2 years |
| Personnel Training and Qualification | Training and qualification of personnel on core maintenance procedures | Every 6-12 months |
Tip 4: Implement a Robust Core Cooling System
A robust core cooling system is essential for removing heat from the nuclear core and preventing overheating. This system typically consists of a primary coolant loop, heat exchangers, and emergency core cooling systems. By implementing a robust core cooling system, operators can ensure that the core is properly cooled and that the risk of overheating is minimized. For example, passive cooling systems can provide a reliable and efficient means of removing heat from the core, even in the event of a loss of power or coolant.
Core Cooling System Components
A robust core cooling system typically consists of several components, including primary coolant pumps, heat exchangers, and emergency core cooling systems. These components work together to provide a reliable and efficient means of removing heat from the core. By carefully selecting and designing these components, operators can ensure that their core cooling system is effective and efficient.
Tip 5: Develop a Comprehensive Emergency Response Plan
A comprehensive emergency response plan is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the nuclear core. This plan should include procedures for responding to emergencies such as loss of coolant, reactor scram, and radioactive release. By developing and implementing a comprehensive emergency response plan, operators can ensure that they are prepared to respond quickly and effectively in the event of an emergency. For instance, regular training and drills can help personnel develop the knowledge and skills needed to respond to emergencies safely and efficiently.
Emergency Response Plan Components
A comprehensive emergency response plan typically consists of several components, including emergency procedures, training and drills, and communication protocols. These components work together to ensure that operators are prepared to respond quickly and effectively in the event of an emergency. By carefully planning and executing these components, operators can ensure that their emergency response plan is effective and efficient.
What is the most critical component of a nuclear core?
+The most critical component of a nuclear core is the fuel assembly, as it is responsible for generating heat through nuclear fission.
How often should the nuclear core be inspected and maintained?
+The nuclear core should be inspected and maintained regularly, with the frequency of inspections and maintenance depending on the specific reactor design and operating conditions.
What is the purpose of a core cooling system?
+The purpose of a core cooling system is to remove heat from the nuclear core and prevent overheating.
Meta Description: Discover the top 5 nuclear core tips for optimizing performance and safety, including fuel assembly design, core monitoring systems, and emergency response planning.