When it comes to the fascinating world of geometry, triangles are one of the most fundamental shapes that have been studied for centuries. Among the various types of triangles, acute and obtuse triangles are two categories that are defined based on the measure of their angles. In this article, we will delve into the world of acute and obtuse triangles, exploring their definitions, properties, and applications in real-world scenarios.
Key Points
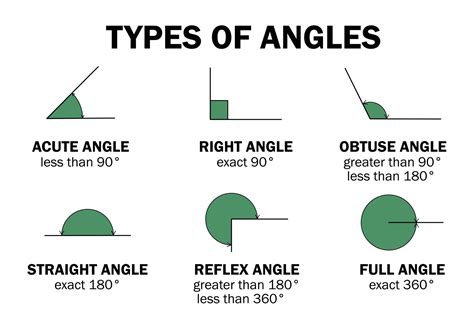
- Acute triangles have all angles less than 90 degrees, with the sum of angles equal to 180 degrees.
- Obtuse triangles have one angle greater than 90 degrees, with the sum of angles equal to 180 degrees.
- The properties of acute and obtuse triangles are crucial in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and physics.
- Understanding the differences between acute and obtuse triangles is essential for solving problems in geometry and trigonometry.
- Real-world applications of acute and obtuse triangles can be seen in the design of buildings, bridges, and electronic circuits.
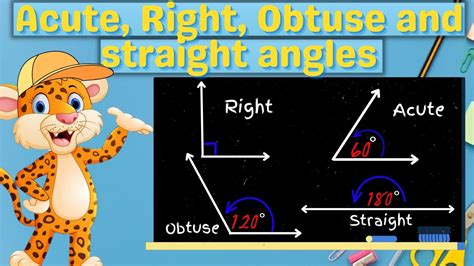
Definition and Properties of Acute Triangles
An acute triangle is a triangle in which all three angles are less than 90 degrees. This means that the largest angle in an acute triangle is less than 90 degrees. Acute triangles can be further classified into different types, such as equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles, based on the length of their sides. The sum of the angles in an acute triangle is always 180 degrees, which is a fundamental property of all triangles.
Properties of Acute Triangles
Acute triangles have several distinct properties that set them apart from other types of triangles. For example, the circumcenter of an acute triangle lies inside the triangle, and the orthocenter lies outside the triangle. Additionally, the altitude of an acute triangle is always shorter than the hypotenuse. These properties are essential in solving problems related to acute triangles and are widely used in various fields, including geometry, trigonometry, and engineering.
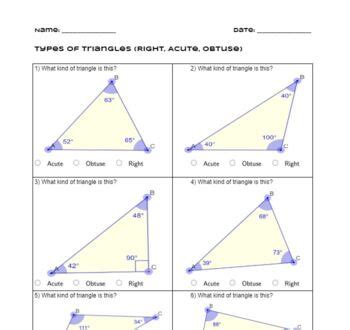
| Type of Triangle | Angle Measure | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Triangle | All angles < 90 degrees | Circumcenter inside, orthocenter outside, altitude < hypotenuse |
| Obtuse Triangle | One angle > 90 degrees | Circumcenter outside, orthocenter inside, altitude > hypotenuse |
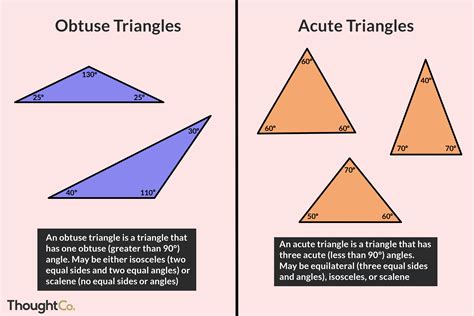
Definition and Properties of Obtuse Triangles
An obtuse triangle is a triangle in which one of the angles is greater than 90 degrees. This means that the largest angle in an obtuse triangle is greater than 90 degrees. Obtuse triangles can also be classified into different types, such as right obtuse, acute obtuse, and equi-obtuse triangles, based on the measure of their angles. The sum of the angles in an obtuse triangle is always 180 degrees, which is a fundamental property of all triangles.
Properties of Obtuse Triangles
Obtuse triangles have several distinct properties that set them apart from other types of triangles. For example, the circumcenter of an obtuse triangle lies outside the triangle, and the orthocenter lies inside the triangle. Additionally, the altitude of an obtuse triangle is always longer than the hypotenuse. These properties are essential in solving problems related to obtuse triangles and are widely used in various fields, including geometry, trigonometry, and engineering.
One of the most interesting properties of obtuse triangles is that they can be used to create complex geometric shapes, such as polyhedra and fractals. These shapes have numerous applications in art, architecture, and design, and are a testament to the beauty and versatility of geometry.
Applications of Acute and Obtuse Triangles
Acute and obtuse triangles have numerous applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, physics, and design. For example, acute triangles are used in the design of bridges, buildings, and electronic circuits, where the stability and strength of the structure are critical. Obtuse triangles, on the other hand, are used in the design of complex geometric shapes, such as polyhedra and fractals, which have numerous applications in art, architecture, and design.
In physics, the properties of acute and obtuse triangles are used to understand the behavior of light and sound waves, which is essential in the design of optical and acoustic systems. Additionally, the properties of acute and obtuse triangles are used in engineering to design and optimize systems, such as mechanical systems, electrical systems, and computer networks.
What is the main difference between an acute triangle and an obtuse triangle?
+The main difference between an acute triangle and an obtuse triangle is the measure of their angles. An acute triangle has all angles less than 90 degrees, while an obtuse triangle has one angle greater than 90 degrees.
What are some common applications of acute triangles?
+Acute triangles have numerous applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, physics, and design. They are used in the design of bridges, buildings, electronic circuits, and mechanical systems, where stability and strength are critical.
What are some common applications of obtuse triangles?
+Obtuse triangles have numerous applications in various fields, including art, architecture, design, and engineering. They are used to create complex geometric shapes, such as polyhedra and fractals, which have numerous applications in design, art, and engineering.
Meta Description: Learn about the properties and applications of acute and obtuse triangles, including their definitions, properties, and real-world uses in architecture, engineering, and design.

![{annotations:[],refusal:null,role:assistant}](https://search.sks.com/assets/img/froggy-style-sex.jpeg)
