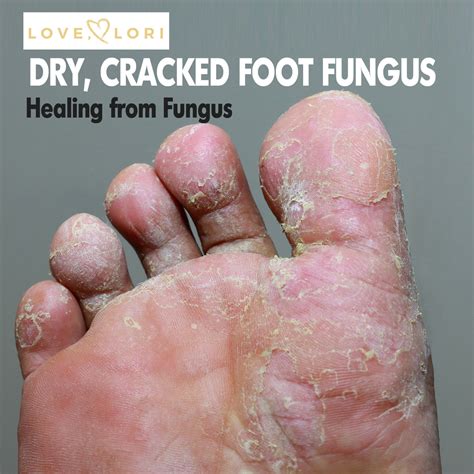
Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the feet. It is characterized by a rash, itching, and cracking of the skin, and can be accompanied by a foul odor. The infection is usually caused by a type of fungus called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments.
Causes and Risk Factors
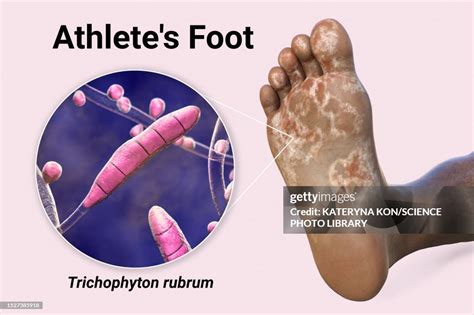
Athlete’s foot is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or by walking barefoot in areas where the fungus is present. The risk of developing athlete’s foot is higher in people who wear tight-fitting shoes, use public showers or locker rooms, or have a weakened immune system. Additionally, people who participate in sports or activities that involve sweating, such as running or hiking, are more likely to develop the infection.
Key Points
- Athlete's foot is a common fungal infection that affects the feet.
- The infection is caused by dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments.
- Risk factors include wearing tight-fitting shoes, using public showers or locker rooms, and having a weakened immune system.
- People who participate in sports or activities that involve sweating are more likely to develop the infection.
- Athlete's foot can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal medications, but severe cases may require prescription-strength treatment.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of athlete’s foot can vary depending on the severity of the infection, but common signs include a red, itchy rash on the feet, especially between the toes, and cracking or peeling of the skin. In some cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the hands or groin area. If left untreated, athlete’s foot can lead to more serious complications, such as cellulitis or abscesses.
| Type of Athlete's Foot | Description |
|---|---|
| Interdigital Athlete's Foot | Affects the skin between the toes, causing itching, burning, and cracking. |
| Moccasin Athlete's Foot | Affects the soles of the feet, causing dryness, scaling, and cracking. |
| Vesicular Athlete's Foot | Characterized by blisters or vesicles on the feet, often accompanied by itching and burning. |
Treatment and Prevention

Treatment for athlete’s foot typically involves over-the-counter antifungal medications, such as creams, powders, or sprays. In severe cases, prescription-strength medications may be necessary. To prevent athlete’s foot, it’s essential to practice good foot hygiene, wear shoes that allow for airflow, and avoid walking barefoot in public areas. Additionally, using antifungal powders or sprays on the feet can help prevent the growth of fungus.
Pictures of Athlete’s Foot Fungus
Looking at pictures of athlete’s foot fungus can help identify the infection and understand its severity. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. Some common characteristics of athlete’s foot fungus include:
- Red, itchy rash on the feet, especially between the toes
- Cracking or peeling of the skin
- Foul odor from the feet
- Scaling or dryness on the soles of the feet
What is the most effective way to treat athlete's foot?
+The most effective way to treat athlete's foot is to use a combination of over-the-counter antifungal medications and practice good foot hygiene, including washing the feet daily and drying them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
How can I prevent athlete's foot?
+To prevent athlete's foot, practice good foot hygiene, wear shoes that allow for airflow, and avoid walking barefoot in public areas. Additionally, using antifungal powders or sprays on the feet can help prevent the growth of fungus.
What are the complications of untreated athlete's foot?
+Untreated athlete's foot can lead to more serious complications, such as cellulitis or abscesses, which can be painful and potentially life-threatening. It's essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
In conclusion, athlete’s foot is a common fungal infection that can be treated and prevented with proper foot hygiene and antifungal medications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to protect themselves from this infection and maintain good foot health. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan if symptoms persist or worsen over time.