The field of biology is vast and encompasses a wide range of products that have revolutionized various aspects of our lives, from healthcare and agriculture to environmental conservation. Understanding these biology products is crucial for appreciating their impact on society and the environment. Here, we delve into five significant biology product definitions, exploring their applications, benefits, and the science behind them.
Biology Products in Modern Society

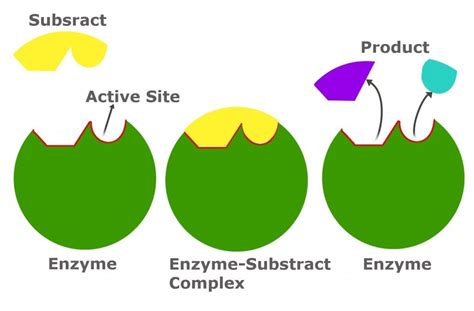
Biology products are derived from living organisms or are inspired by biological processes. They have transformed industries such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology, offering solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing challenges. The development and application of these products are based on deep knowledge of biological systems, genetic engineering, and molecular biology.
1. Vaccines
Vaccines are biological preparations that provide active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. They typically contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. By stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and fight pathogens, vaccines prevent diseases and have been instrumental in controlling and eliminating infectious diseases such as smallpox, polio, and measles. The production of vaccines involves advanced biotechnology techniques, including genetic engineering and cell culture methods.
| Vaccine Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Inactivated Vaccines | Contain killed pathogens |
| Live, Attenuated Vaccines | Contain weakened pathogens |
| Subunit Vaccines | Contain only components of pathogens (e.g., proteins) |
2. Recombinant Insulin
Recombinant insulin is a synthetic form of human insulin produced through genetic engineering. By inserting the human gene for insulin into bacteria, such as E. coli, or yeast, these microorganisms can produce insulin that is identical to the natural human hormone. Recombinant insulin has revolutionized the treatment of diabetes, providing a consistent and reliable source of insulin for patients worldwide. This technology has also paved the way for the production of other therapeutic proteins.
3. Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) in Agriculture
GMOs, or genetically modified organisms, are plants, animals, or microorganisms whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. In agriculture, GMOs are designed to introduce desirable traits such as resistance to pests, improved nutritional content, or the ability to thrive in challenging environmental conditions. The use of GMOs in agriculture aims to increase crop yields, reduce pesticide use, and improve food security. However, the deployment of GMOs is subject to rigorous safety assessments and regulatory approvals due to concerns about their potential impact on the environment and human health.
4. Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut flora. They are found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, as well as in dietary supplements. Probiotics can help maintain a healthy digestive system, boost the immune system, and even produce vitamins. The effectiveness of probiotics can vary depending on the strain of the microorganism, the condition being treated, and the individual’s health status.
5. Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics are materials that can break down naturally in the environment, typically by the action of microorganisms. These plastics are often made from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or potato starch. Unlike traditional plastics that are derived from petroleum and can persist in the environment for centuries, biodegradable plastics offer a more sustainable alternative, reducing plastic waste and the harmful effects of plastic pollution on ecosystems.
Key Points
- Vaccines are crucial for preventing infectious diseases and have significantly improved public health.
- Recombinant insulin, produced through genetic engineering, has revolutionized diabetes treatment.
- GMOs in agriculture aim to improve crop yields and food security but require careful assessment of their environmental and health impacts.
- Probiotics can enhance digestive health and immune function by restoring the balance of gut flora.
- Biodegradable plastics provide a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, reducing environmental pollution.
In conclusion, biology products have diverse applications and contribute significantly to advancements in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental sustainability. The development and use of these products are based on a deep understanding of biological principles and technologies such as genetic engineering and biotechnology. As research and innovation continue, we can expect even more impactful biology products to emerge, addressing some of the world's most pressing challenges.
What are the benefits of using biodegradable plastics over traditional plastics?
+Biodegradable plastics reduce environmental pollution by breaking down naturally, unlike traditional plastics that can persist for centuries, harming ecosystems and wildlife.
How do vaccines contribute to public health?
+Vaccines prevent infectious diseases, reducing morbidity and mortality rates. They have been instrumental in controlling and eliminating diseases such as smallpox and polio, significantly improving public health worldwide.
What are the potential risks associated with GMOs in agriculture?
+Potential risks include unintended effects on the environment, such as the development of pesticide-resistant pests, and concerns about the safety of GMOs for human consumption. Rigorous testing and regulation are essential to mitigate these risks.