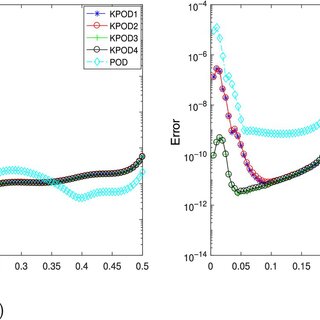
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) is a dimensionality reduction technique used to analyze and simplify complex systems by extracting the most dominant features or patterns. This method has been widely applied in various fields, including fluid dynamics, signal processing, and image analysis. The core idea behind POD is to decompose a high-dimensional dataset into a set of orthogonal modes, which can be used to reconstruct the original data with a desired level of accuracy. In this article, we will delve into the details of POD, its mathematical formulation, and its applications in different domains.
Key Points
- POD is a dimensionality reduction technique used to simplify complex systems.
- It extracts the most dominant features or patterns from a high-dimensional dataset.
- POD has been applied in various fields, including fluid dynamics, signal processing, and image analysis.
- The technique involves decomposing data into a set of orthogonal modes.
- POD can be used for data compression, feature extraction, and noise reduction.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
The mathematical formulation of POD involves the use of singular value decomposition (SVD) or eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) to extract the orthogonal modes from a given dataset. The SVD of a matrix A can be written as A = UΣV^T, where U and V are orthogonal matrices, and Σ is a diagonal matrix containing the singular values of A. The columns of U and V represent the left and right singular vectors of A, respectively. In the context of POD, the left singular vectors of A are used as the orthogonal modes, and the corresponding singular values represent the energy or importance of each mode.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
The application of POD in fluid dynamics is a prominent example of its usefulness. In this field, POD is used to analyze the behavior of complex flow systems, such as turbulent flows or flows with complex geometries. By applying POD to a dataset of flow snapshots, researchers can extract the most dominant features or patterns of the flow, which can be used to reconstruct the original flow field with a desired level of accuracy. This can be particularly useful for reducing the computational cost of simulating complex flow systems or for identifying the most important features of the flow that contribute to its overall behavior.
| POD Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Fluid Dynamics | Analysis of complex flow systems, such as turbulent flows or flows with complex geometries. |
| Signal Processing | Feature extraction and noise reduction in signals, such as audio or image signals. |
| Image Analysis | Image compression and feature extraction, such as in image recognition or object detection tasks. |
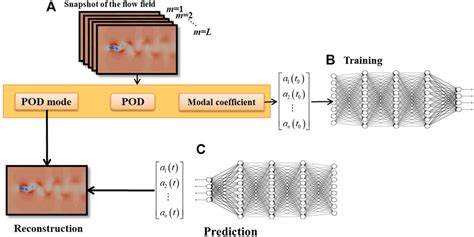
POD Algorithm and Implementation
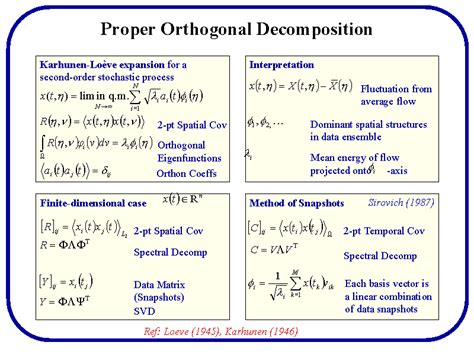
The POD algorithm involves the following steps: (1) collection of a dataset of snapshots, (2) computation of the correlation matrix or covariance matrix of the dataset, (3) computation of the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the correlation matrix or covariance matrix, and (4) selection of the most important modes based on their corresponding eigenvalues. The resulting modes can be used for a variety of purposes, including data compression, feature extraction, and noise reduction.
Technical Specifications and Considerations
When implementing POD, it is essential to consider the size and complexity of the dataset, as well as the computational resources available. The choice of the correlation matrix or covariance matrix depends on the nature of the data and the specific application. Additionally, the selection of the number of modes to retain is critical, as it determines the trade-off between the accuracy of the reconstruction and the complexity of the resulting model. In some cases, it may be necessary to use additional techniques, such as data normalization or data transformation, to preprocess the data before applying POD.
In conclusion, Proper Orthogonal Decomposition is a powerful technique for analyzing and simplifying complex systems. Its applications in various fields, including fluid dynamics, signal processing, and image analysis, have demonstrated its usefulness in extracting the most dominant features or patterns from high-dimensional datasets. By understanding the mathematical formulation and implementation of POD, researchers and practitioners can leverage this technique to gain insights into complex systems and develop more efficient models and algorithms.
What is the main purpose of Proper Orthogonal Decomposition?
+The main purpose of Proper Orthogonal Decomposition is to reduce the dimensionality of a complex system by extracting the most dominant features or patterns from a high-dimensional dataset.
How is POD applied in fluid dynamics?
+In fluid dynamics, POD is used to analyze the behavior of complex flow systems, such as turbulent flows or flows with complex geometries, by extracting the most dominant features or patterns of the flow.
What is the energy criterion in POD?
+The energy criterion in POD involves retaining the modes that capture a certain percentage of the total energy of the system, which determines the trade-off between the accuracy of the reconstruction and the complexity of the resulting model.