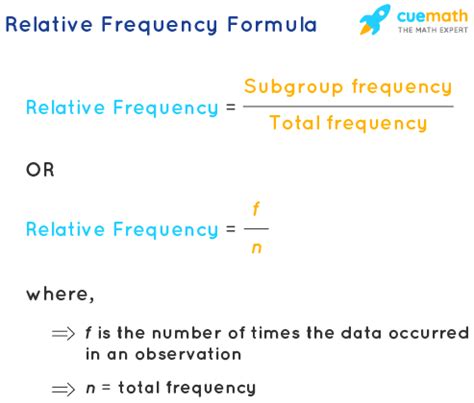
The relative frequency formula is a statistical tool used to analyze and understand the distribution of data within a dataset. It is a measure of the frequency of a particular data point or category relative to the total number of data points in the dataset. In essence, it helps to identify how often a specific value or range of values occurs within the dataset. The relative frequency formula is calculated as the ratio of the frequency of a particular data point or category to the total number of data points in the dataset, usually expressed as a percentage or proportion.
To calculate the relative frequency, one must first determine the frequency of each data point or category within the dataset. This can be achieved by counting the number of times each value or category appears. Once the frequencies are determined, the relative frequency can be calculated using the formula: Relative Frequency = (Frequency of the data point or category / Total number of data points) * 100. This formula provides a clear and concise way to express the frequency of each data point or category in relation to the total dataset.
Key Points
- The relative frequency formula is used to analyze the distribution of data within a dataset.
- It is calculated as the ratio of the frequency of a particular data point or category to the total number of data points.
- The formula is expressed as: Relative Frequency = (Frequency of the data point or category / Total number of data points) * 100.
- Relative frequency is usually expressed as a percentage or proportion.
- It helps to identify how often a specific value or range of values occurs within the dataset.
Understanding the Relative Frequency Formula

The relative frequency formula is an essential tool in statistics, as it allows researchers to understand the distribution of data and identify patterns or trends. By calculating the relative frequency of each data point or category, researchers can determine which values or categories are most common and which are least common. This information can be used to inform decisions, identify areas for further study, and develop predictive models.
Calculating Relative Frequency
To calculate the relative frequency, follow these steps:
- Determine the frequency of each data point or category within the dataset.
- Calculate the total number of data points in the dataset.
- Use the formula: Relative Frequency = (Frequency of the data point or category / Total number of data points) * 100.
| Category | Frequency | Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| A | 20 | 40% |
| B | 15 | 30% |
| C | 10 | 20% |
| D | 5 | 10% |
Applications of Relative Frequency
The relative frequency formula has numerous applications in various fields, including business, medicine, social sciences, and engineering. It is used to analyze customer behavior, understand disease prevalence, identify trends in social media, and optimize system performance. By applying the relative frequency formula, professionals can gain valuable insights into their data, make informed decisions, and drive business success.
Real-World Examples
For instance, a marketing firm might use the relative frequency formula to analyze customer purchase behavior. By calculating the relative frequency of each product category, the firm can identify which products are most popular and adjust their marketing strategies accordingly. Similarly, a healthcare professional might use the relative frequency formula to understand the prevalence of a particular disease within a population. By analyzing the relative frequency of the disease, the professional can identify high-risk groups and develop targeted interventions.
In conclusion, the relative frequency formula is a powerful tool for analyzing and understanding the distribution of data within a dataset. By applying this formula, professionals can gain valuable insights into their data, make informed decisions, and drive business success. Whether in business, medicine, social sciences, or engineering, the relative frequency formula is an essential tool for anyone working with data.
What is the purpose of the relative frequency formula?
+The purpose of the relative frequency formula is to analyze and understand the distribution of data within a dataset. It helps to identify how often a specific value or range of values occurs within the dataset.
How is the relative frequency formula calculated?
+The relative frequency formula is calculated as the ratio of the frequency of a particular data point or category to the total number of data points in the dataset, usually expressed as a percentage or proportion.
What are the applications of the relative frequency formula?
+The relative frequency formula has numerous applications in various fields, including business, medicine, social sciences, and engineering. It is used to analyze customer behavior, understand disease prevalence, identify trends in social media, and optimize system performance.