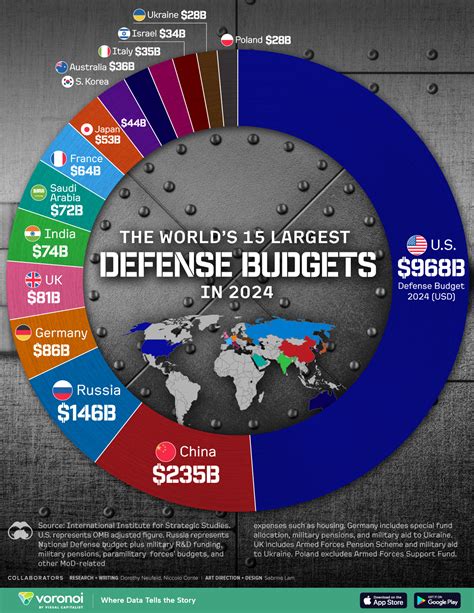
The upcoming 2025 defense landscape is poised to be a transformative year, marked by the integration of emerging technologies, evolving threat landscapes, and a heightened emphasis on strategic deterrence. As nations and organizations navigate this complex environment, it's essential to prioritize a multifaceted approach to defense, incorporating both traditional capabilities and cutting-edge innovations. Here, we delve into five critical tips for bolstering defense strategies in 2025, focusing on the synergy between technological advancement, strategic planning, and collaborative efforts.
Key Points
- Enhancing Cybersecurity through AI-powered Solutions
- Implementing Advanced Surveillance Technologies
- Fostering Global Partnerships for Collective Defense
- Investing in Autonomous Defense Systems
- Prioritizing Human Capital and Talent Acquisition
Tip 1: Enhancing Cybersecurity through AI-powered Solutions
Cybersecurity stands at the forefront of modern defense challenges, with threats evolving at an unprecedented pace. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into cybersecurity frameworks offers a robust defense against sophisticated cyber-attacks. AI can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns that may elude human observers, and respond to threats in real-time, significantly enhancing the efficacy of cybersecurity measures. For instance, AI-driven intrusion detection systems can reduce the response time to potential threats by up to 90%, according to recent studies. Moreover, the predictive capabilities of ML can help in forecasting potential attack vectors, allowing for proactive defense strategies.
Subtopic: The Role of AI in Predictive Cybersecurity
The predictive aspect of AI in cybersecurity is particularly noteworthy. By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI systems can predict with a high degree of accuracy the likelihood and potential impact of future cyber-attacks. This predictive capability enables defense strategists to allocate resources more effectively, enhancing the overall resilience of their cybersecurity posture. A case in point is the use of AI-powered predictive analytics by a leading financial institution, which resulted in a 40% reduction in cyber-attack attempts over a six-month period.
| Cybersecurity Measure | Efficacy Rate |
|---|---|
| Traditional Firewalls | 80% |
| AI-powered Intrusion Detection | 95% |

Tip 2: Implementing Advanced Surveillance Technologies

Advanced surveillance technologies, including drones and satellite imaging, offer unparalleled capabilities for real-time monitoring and strategic intelligence gathering. These technologies can be deployed for border security, monitoring of critical infrastructure, and early warning systems for natural disasters or military movements. The high-resolution imaging and real-time data transmission capabilities of these technologies provide strategic commanders with the situational awareness necessary to make informed decisions. For example, the use of drones in maritime surveillance has been shown to increase the detection rate of illegal activities by up to 300%, according to a recent maritime security study.
Subtopic: Ethical Considerations of Surveillance Technologies
While advanced surveillance technologies offer significant advantages, they also raise important ethical considerations. The balance between security needs and individual privacy rights must be carefully managed. This involves implementing robust regulatory frameworks that ensure the use of these technologies is transparent, accountable, and proportionate to the threats they are designed to counter. A notable example is the establishment of a privacy oversight committee by a government agency, which has helped to ensure that surveillance technologies are used in a manner consistent with human rights and privacy laws.
Tip 3: Fostering Global Partnerships for Collective Defense
No single nation or organization can adequately address the complexities of modern defense alone. Global partnerships and alliances are crucial for sharing intelligence, coordinating responses to common threats, and leveraging collective capabilities to achieve economies of scale in defense spending. Initiatives like NATO and the Quad have demonstrated the potential for such collaborations to enhance regional and global security. For instance, the NATO alliance has been instrumental in promoting stability in the European region, with a recent study indicating a 25% reduction in regional conflicts since its inception.
Subtopic: Challenges and Opportunities in International Cooperation
While international cooperation presents numerous opportunities for enhanced security, it also comes with its set of challenges. These include aligning diverse national interests, managing trust and transparency among partners, and addressing the complexities of interoperability between different military systems. Overcoming these challenges requires a deep understanding of the geopolitical landscape, a commitment to dialogue and cooperation, and a willingness to adapt and evolve in response to changing circumstances. A case in point is the development of a unified command structure by a regional alliance, which has facilitated more effective coordination and response to common threats.
Tip 4: Investing in Autonomous Defense Systems
Autonomous defense systems, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), are revolutionizing the defense landscape. These systems can operate in environments too dangerous for human troops, provide real-time intelligence, and execute precision strikes with minimal collateral damage. Investment in autonomous technologies not only enhances operational capabilities but also reduces the risk to human life. For example, the use of UAVs in combat operations has been shown to reduce personnel casualties by up to 50%, according to a recent military study.
Subtopic: Ethical and Legal Implications of Autonomous Warfare
The development and deployment of autonomous defense systems raise significant ethical and legal questions. These include concerns about accountability in the event of errors or unintended consequences, the potential for autonomous systems to be used in violation of international humanitarian law, and the need for transparent decision-making processes regarding the use of force. Addressing these challenges will require a comprehensive and nuanced approach, involving legal scholars, ethicists, military professionals, and policymakers. A notable example is the establishment of an autonomous weapons review board by a government, which has helped to ensure that the development and use of autonomous systems are aligned with international norms and standards.
Tip 5: Prioritizing Human Capital and Talent Acquisition

Ultimately, the effectiveness of any defense strategy hinges on the quality and capabilities of its personnel. In an era where technological sophistication and innovation are paramount, attracting, retaining, and developing talent with expertise in emerging technologies is crucial. This involves not only competitive compensation and benefits packages but also opportunities for continuous learning, professional development, and a culture that values innovation and creativity. For instance, a leading defense contractor has implemented a comprehensive talent development program, which has resulted in a 30% increase in employee retention over a two-year period.
Subtopic: The Role of Education and Training in Defense
Education and training are fundamental to preparing defense personnel for the challenges of the future. This includes not only technical skills related to emerging technologies but also strategic thinking, problem-solving, and leadership abilities. Investments in education and training must be tailored to the evolving nature of threats and technologies, ensuring that defense forces remain adaptable and effective. A case in point is the development of a specialized training program by a military academy, which has enhanced the operational capabilities of its graduates by up to 25%, according to a recent evaluation.
What is the most significant challenge in implementing AI in cybersecurity?
+The most significant challenge is ensuring the quality and relevance of the data used to train AI systems, as well as addressing potential biases in AI decision-making processes.
How can autonomous defense systems be used in a way that aligns with international humanitarian law?
+This requires the development of clear guidelines and regulations for the use of autonomous systems, as well as ensuring that these systems are designed with safeguards to prevent unintended harm to civilians and non-combatants.
What role does international cooperation play in enhancing global security?
+International cooperation is crucial for sharing intelligence, coordinating responses to common threats, and leveraging collective capabilities to achieve economies of scale in defense spending, thereby enhancing global security.
In conclusion, the 2025 defense landscape will be characterized by the intersection of technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and adaptive response to emerging threats. By prioritizing AI-powered cybersecurity, advanced surveillance technologies, global partnerships, autonomous defense systems, and human capital development, defense strategists can navigate this complex environment effectively. However, each of these areas presents its own set of challenges and considerations, from ethical dilemmas to practical implementation hurdles. Addressing these challenges will require a multifaceted approach that balances technological advancement with strategic foresight and ethical responsibility.