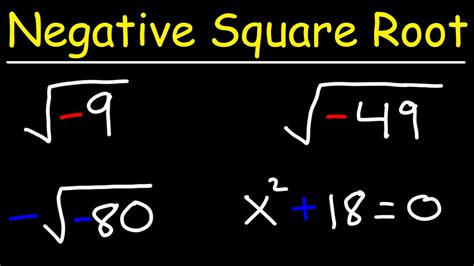
The concept of square roots of negative numbers has been a subject of interest and debate among mathematicians and scientists for centuries. The idea of taking the square root of a negative number may seem counterintuitive at first, as the square of any real number is always non-negative. However, with the introduction of imaginary numbers, mathematicians were able to extend the real number system to include complex numbers, which enabled the calculation of square roots of negative numbers. In this article, we will delve into the history, mathematical foundations, and practical applications of square roots of negative numbers.
Introduction to Imaginary Numbers

The concept of imaginary numbers was first introduced by Italian mathematician Girolamo Cardano in the 16th century. Cardano, who is also known for his work on probability theory and algebra, proposed the idea of imaginary numbers as a way to extend the real number system to include roots of negative numbers. The concept was later developed and formalized by other mathematicians, including Leonhard Euler and Carl Friedrich Gauss. Today, imaginary numbers are a fundamental part of complex analysis and are used in a wide range of mathematical and scientific applications.
Definition and Properties of Imaginary Numbers
An imaginary number is defined as a number of the form ai, where a is a real number and i is the imaginary unit, which satisfies the equation i^2 = -1. The imaginary unit i can be thought of as a mathematical construct that allows us to extend the real number system to include roots of negative numbers. The properties of imaginary numbers are similar to those of real numbers, with the addition of the fact that i^2 = -1. This means that imaginary numbers can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided, just like real numbers, but with the added complexity of dealing with the imaginary unit i.
| Operation | Example |
|---|---|
| Addition | $(2i) + (3i) = 5i$ |
| Subtraction | $(4i) - (2i) = 2i$ |
| Multiplication | $(2i) \cdot (3i) = -6$ |
| Division | $(4i) / (2i) = 2$ |

Calculating Square Roots of Negative Numbers
Now that we have introduced the concept of imaginary numbers, we can proceed to calculate the square roots of negative numbers. The square root of a negative number can be calculated using the formula \sqrt{-x} = i\sqrt{x}, where x is a positive real number. For example, the square root of -4 can be calculated as \sqrt{-4} = i\sqrt{4} = 2i. Similarly, the square root of -9 can be calculated as \sqrt{-9} = i\sqrt{9} = 3i.
Examples and Applications
The concept of square roots of negative numbers has numerous practical applications in fields such as electrical engineering, signal processing, and quantum mechanics. For example, in electrical engineering, imaginary numbers are used to represent the impedance of circuits, which can be used to calculate the voltage and current of the circuit. In signal processing, imaginary numbers are used to represent the frequency response of filters, which can be used to remove noise and other unwanted signals from a signal. In quantum mechanics, imaginary numbers are used to represent the wave function of particles, which can be used to calculate the probability of finding a particle in a particular state.
Key Points
- The concept of imaginary numbers was first introduced by Italian mathematician Girolamo Cardano in the 16th century.
- Imaginary numbers are defined as numbers of the form $ai$, where $a$ is a real number and $i$ is the imaginary unit.
- The square root of a negative number can be calculated using the formula $\sqrt{-x} = i\sqrt{x}$, where $x$ is a positive real number.
- The concept of square roots of negative numbers has numerous practical applications in fields such as electrical engineering, signal processing, and quantum mechanics.
- Imaginary numbers are used to represent the impedance of circuits, the frequency response of filters, and the wave function of particles.
In conclusion, the concept of square roots of negative numbers is a fundamental part of complex analysis and has numerous practical applications in fields such as electrical engineering, signal processing, and quantum mechanics. The introduction of imaginary numbers has enabled mathematicians and scientists to extend the real number system to include roots of negative numbers, which has led to numerous breakthroughs and discoveries in these fields. As we continue to explore and develop new mathematical and scientific concepts, the importance of imaginary numbers and square roots of negative numbers will only continue to grow.
What is the definition of an imaginary number?
+An imaginary number is defined as a number of the form ai, where a is a real number and i is the imaginary unit, which satisfies the equation i^2 = -1.
How do you calculate the square root of a negative number?
+The square root of a negative number can be calculated using the formula \sqrt{-x} = i\sqrt{x}, where x is a positive real number.
What are some practical applications of imaginary numbers and square roots of negative numbers?
+Imaginary numbers and square roots of negative numbers have numerous practical applications in fields such as electrical engineering, signal processing, and quantum mechanics, including representing the impedance of circuits, the frequency response of filters, and the wave function of particles.