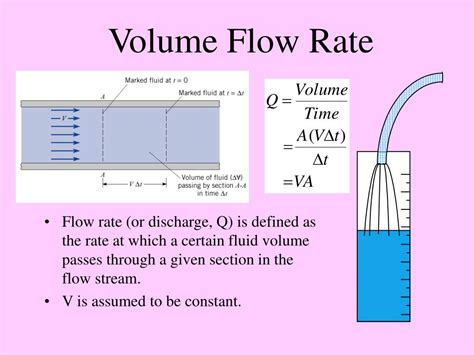
The concept of volumetric flow rate is a fundamental principle in various fields, including physics, engineering, and chemistry. It is defined as the volume of fluid that flows through a given surface per unit time. In other words, it is a measure of the rate at which a fluid flows through a pipe, channel, or other conduit. Understanding volumetric flow rate is crucial in designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow, such as pipelines, pumps, and turbines.
In everyday life, we often encounter examples of volumetric flow rate, from the water flowing through a showerhead to the air flowing through a ventilation system. The volumetric flow rate can be calculated using the formula: Q = A \* v, where Q is the volumetric flow rate, A is the cross-sectional area of the pipe or conduit, and v is the velocity of the fluid. This formula highlights the importance of both the area and velocity in determining the volumetric flow rate.
Key Points
- The volumetric flow rate is a measure of the volume of fluid that flows through a given surface per unit time.
- It is calculated using the formula: Q = A \* v, where Q is the volumetric flow rate, A is the cross-sectional area, and v is the velocity of the fluid.
- Understanding volumetric flow rate is crucial in designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow.
- Volumetric flow rate is used in various applications, including pipeline design, pump selection, and turbine optimization.
- It is an important parameter in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of systems that involve fluid flow.
Volumetric Flow Rate Calculation and Applications
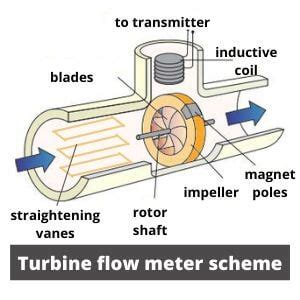
The calculation of volumetric flow rate is a straightforward process that involves measuring the cross-sectional area of the pipe or conduit and the velocity of the fluid. The velocity can be measured using various techniques, such as pitot tubes, anemometers, or Doppler velocimetry. Once the velocity is known, the volumetric flow rate can be calculated using the formula: Q = A * v. This calculation is essential in various applications, including pipeline design, pump selection, and turbine optimization.
In pipeline design, the volumetric flow rate is used to determine the required diameter and material of the pipe. A higher volumetric flow rate requires a larger pipe diameter to ensure that the fluid flows efficiently and safely. In pump selection, the volumetric flow rate is used to determine the required pump capacity and type. A pump that is designed to handle a higher volumetric flow rate is required for applications that involve large volumes of fluid.
Volumetric Flow Rate in Turbine Optimization
In turbine optimization, the volumetric flow rate is used to determine the required turbine size and type. A turbine that is designed to handle a higher volumetric flow rate is required for applications that involve large volumes of fluid. The volumetric flow rate is also used to optimize the performance of the turbine, ensuring that it operates efficiently and safely. By optimizing the volumetric flow rate, turbine operators can increase the power output and reduce the risk of damage or failure.
| Application | Volumetric Flow Rate Range |
|---|---|
| Pipeline design | 0.01-100 m3/s |
| Pump selection | 0.1-1000 m3/s |
| Turbine optimization | 1-10000 m3/s |

Volumetric Flow Rate Measurement Techniques
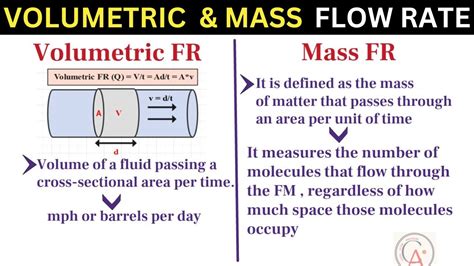
There are various techniques used to measure volumetric flow rate, including differential pressure measurement, velocity measurement, and volumetric measurement. Differential pressure measurement involves measuring the pressure difference between two points in the pipe or conduit, which is proportional to the volumetric flow rate. Velocity measurement involves measuring the velocity of the fluid using techniques such as pitot tubes or anemometers, which can be used to calculate the volumetric flow rate.
Volumetric measurement involves measuring the volume of fluid that flows through a given surface per unit time, which can be done using techniques such as flow meters or volumetric tanks. Each technique has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of technique depends on the specific application and requirements. By selecting the appropriate measurement technique, engineers and operators can accurately measure the volumetric flow rate and optimize the performance of systems that involve fluid flow.
Common Challenges in Volumetric Flow Rate Measurement
There are several challenges associated with measuring volumetric flow rate, including accuracy, reliability, and cost. The accuracy of the measurement technique is critical in ensuring that the volumetric flow rate is measured correctly, which can be affected by factors such as pipe roughness, fluid properties, and measurement uncertainty. The reliability of the measurement technique is also important, as it can affect the overall performance and safety of the system.
The cost of the measurement technique is another important consideration, as it can affect the overall cost of the system. By selecting a measurement technique that balances accuracy, reliability, and cost, engineers and operators can ensure that the volumetric flow rate is measured correctly and efficiently. Additionally, advances in technology have led to the development of more accurate and reliable measurement techniques, such as ultrasonic flow meters and Coriolis flow meters, which can provide accurate and reliable measurements of volumetric flow rate.
What is the significance of volumetric flow rate in pipeline design?
+The volumetric flow rate is significant in pipeline design as it determines the required diameter and material of the pipe. A higher volumetric flow rate requires a larger pipe diameter to ensure that the fluid flows efficiently and safely.
How is volumetric flow rate measured in turbine optimization?
+The volumetric flow rate is measured in turbine optimization using techniques such as differential pressure measurement, velocity measurement, or volumetric measurement. The choice of technique depends on the specific application and requirements.
What are the common challenges in volumetric flow rate measurement?
+The common challenges in volumetric flow rate measurement include accuracy, reliability, and cost. The accuracy of the measurement technique is critical in ensuring that the volumetric flow rate is measured correctly, while the reliability and cost of the technique can affect the overall performance and safety of the system.
In conclusion, the volumetric flow rate is a critical parameter in various fields, including physics, engineering, and chemistry. Understanding the principles of volumetric flow rate and its applications is essential in designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow. By selecting the appropriate measurement technique and considering the challenges associated with volumetric flow rate measurement, engineers and operators can ensure that the volumetric flow rate is measured correctly and efficiently, leading to improved performance and safety of systems that involve fluid flow.