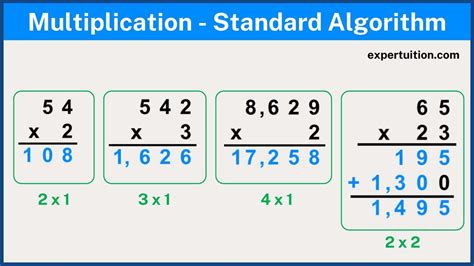
Mastering the standard algorithm for multiplication is a crucial milestone in the journey of mathematical development for students. This fundamental operation, while seemingly straightforward, can often pose challenges for young learners due to its abstract nature and the necessity for precise step-by-step execution. The standard algorithm for multiplication, a method universally taught and applied, involves a series of steps that, when followed meticulously, yield accurate results. This article aims to demystify the process, making it accessible and understandable for both students and educators alike, thereby facilitating a deeper grasp of mathematical concepts and their practical applications.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of multiplication as repeated addition or arrays.
- Mastery of the standard algorithm involves precise execution of steps.
- Importance of place value understanding in the multiplication algorithm.
- Using real-world examples to illustrate the practical application of multiplication.
- Developing problem-solving skills through varied multiplication exercises.
Introduction to Standard Algorithm Multiplication

The standard algorithm for multiplication is based on the principle of breaking down numbers into their place values (ones, tens, hundreds, etc.) and then performing multiplication on these parts before combining the results. This method leverages the distributive property of multiplication over addition, making the calculation process systematic and efficient. For instance, when multiplying 43 by 27, one would break down 43 into 40 and 3, and 27 into 20 and 7, and then perform the multiplication for each part before adding up the results.
Understanding Place Value in Multiplication
A critical component of the standard algorithm is the understanding of place value. Each digit in a number has a place value (ones, tens, hundreds), and when multiplying, the placement of the partial products is determined by these place values. For example, in multiplying 14 by 25, the partial product of 14 (10 + 4) times 25 would be calculated by multiplying 10 * 25 and 4 * 25, resulting in 250 and 100, respectively, before being added together to get 350. The accuracy of the final result depends heavily on correctly aligning these partial products based on their place values.
| Place Value | Partial Product |
|---|---|
| Tens | 10 * 25 = 250 |
| Ones | 4 * 25 = 100 |

Practical Applications and Real-World Examples

Multiplication is not merely an abstract mathematical operation; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life. For instance, calculating the area of a room, determining the total cost of items, or figuring out the number of seats in a theater all involve multiplication. Using real-world examples to illustrate the standard algorithm can help students see the relevance and utility of what they are learning, thereby enhancing their motivation and engagement with the subject matter.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Beyond merely executing the standard algorithm, developing problem-solving skills is essential for a deep understanding of multiplication. This involves presenting students with a variety of multiplication problems, including those that require breaking down complex numbers into simpler components for easier calculation. For example, multiplying 48 by 17 can be approached by breaking down 48 into 40 and 8, and then multiplying each by 17, before adding the results together. Such exercises not only reinforce the standard algorithm but also foster critical thinking and analytical skills.
| Problem | Solution Approach |
|---|---|
| 48 * 17 | Break down 48 into 40 and 8, then multiply each by 17 |
What is the importance of understanding place value in multiplication?
+Understanding place value is crucial because it determines the correct alignment and calculation of partial products, ensuring the accuracy of the final result in multiplication.
How can real-world examples help in learning multiplication?
+Real-world examples make multiplication more relatable and interesting, helping students understand its practical applications and relevance, thereby enhancing their engagement and motivation to learn.
What role does the standard algorithm play in developing problem-solving skills?
+The standard algorithm provides a systematic approach to multiplication, allowing students to develop problem-solving skills through the application of this method to various problems, including those that require decomposition and recomposition of numbers.
In conclusion, mastering the standard algorithm for multiplication is a fundamental step in mathematical education, offering a systematic and efficient method for performing multiplication tasks. By understanding the underlying principles, such as place value and the distributive property, and by applying these concepts to real-world examples and varied problem-solving exercises, students can develop a deep and lasting grasp of multiplication. This, in turn, lays the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and equips individuals with the analytical and critical thinking skills necessary for success in an increasingly complex and data-driven world.