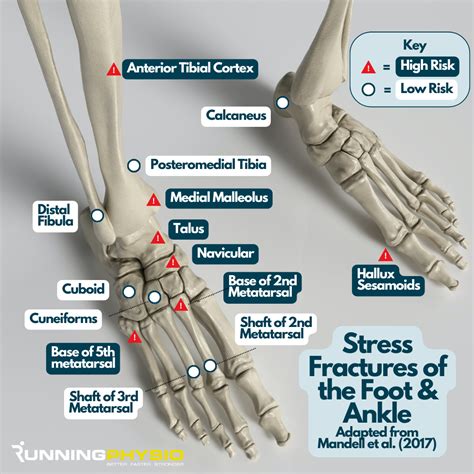
A stress fracture in the ankle is a common overuse injury that occurs when there is a small crack in one of the bones in the ankle. This type of injury is often seen in athletes who participate in sports that involve running, jumping, or repetitive landing, such as basketball, soccer, and track and field. Stress fractures can also occur in individuals who have recently increased their physical activity or changed their exercise routine. The ankle is a complex joint that consists of three bones: the tibia, fibula, and talus. The tibia and fibula are the two long bones that make up the lower leg, and the talus is a small bone that connects the leg bones to the foot.
The causes of stress fractures in the ankle are multifactorial and can include repetitive stress, poor foot mechanics, and inadequate training. When an individual participates in repetitive activities, such as running or jumping, it can cause tiny cracks in the bone. If the bone is not given time to heal, these cracks can grow and eventually lead to a stress fracture. Poor foot mechanics, such as overpronation or supination, can also contribute to the development of a stress fracture. Additionally, inadequate training, such as suddenly increasing the intensity or duration of physical activity, can put excessive stress on the ankle bones and lead to a stress fracture.
Key Points
- A stress fracture in the ankle is a common overuse injury that occurs when there is a small crack in one of the bones in the ankle.
- The causes of stress fractures in the ankle are multifactorial and can include repetitive stress, poor foot mechanics, and inadequate training.
- Symptoms of a stress fracture in the ankle can include pain, swelling, and bruising.
- Diagnosis of a stress fracture in the ankle typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays or an MRI.
- Treatment of a stress fracture in the ankle typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation, as well as physical therapy and bracing.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
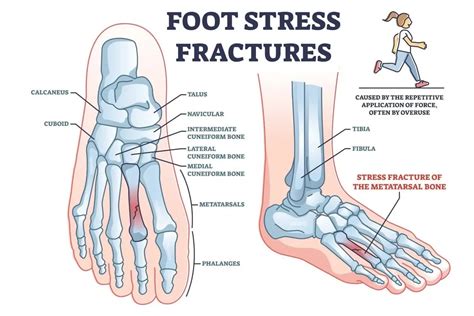
Symptoms of a stress fracture in the ankle can include pain, swelling, and bruising. The pain is often localized to a specific area and can be worse with weight-bearing activities. In some cases, the pain may be severe enough to limit an individual’s ability to participate in physical activities. A physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays or an MRI, are typically used to diagnose a stress fracture in the ankle. During the physical examination, the healthcare provider will assess the ankle for tenderness, swelling, and bruising. Imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of symptoms.
Treatment Options
Treatment of a stress fracture in the ankle typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). This can help reduce pain and inflammation and promote healing. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve ankle strength and flexibility. In some cases, bracing or casting may be necessary to provide additional support and protection to the ankle. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as untreated stress fractures can lead to more severe complications, such as a complete fracture or chronic pain.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| RICE | Rest, ice, compression, and elevation to reduce pain and inflammation |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises to improve ankle strength and flexibility |
| Bracing or Casting | Additional support and protection to the ankle |
| Pain Management | Medications to reduce pain and inflammation |
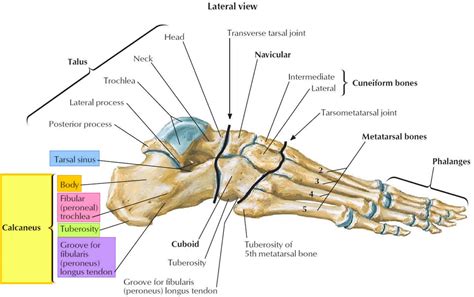
Prevention and Recovery

Prevention of stress fractures in the ankle involves a combination of proper training, equipment, and technique. Individuals who participate in sports or physical activities should gradually increase their intensity and duration to avoid putting excessive stress on the ankle bones. Proper footwear and orthotics can also help reduce the risk of stress fractures. Recovery from a stress fracture in the ankle can take several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury. It is essential to follow a comprehensive treatment plan and avoid activities that can exacerbate the injury.
Complications and Long-term Effects
Untreated stress fractures in the ankle can lead to more severe complications, such as a complete fracture or chronic pain. In some cases, stress fractures can also lead to long-term effects, such as arthritis or limited mobility. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time to prevent these complications and promote optimal recovery.
What are the symptoms of a stress fracture in the ankle?
+Symptoms of a stress fracture in the ankle can include pain, swelling, and bruising. The pain is often localized to a specific area and can be worse with weight-bearing activities.
How is a stress fracture in the ankle diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of a stress fracture in the ankle typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays or an MRI.
What are the treatment options for a stress fracture in the ankle?
+Treatment of a stress fracture in the ankle typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and bracing or casting.
Meta Description: A stress fracture in the ankle is a common overuse injury that occurs when there is a small crack in one of the bones in the ankle. Learn about the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention of stress fractures in the ankle.