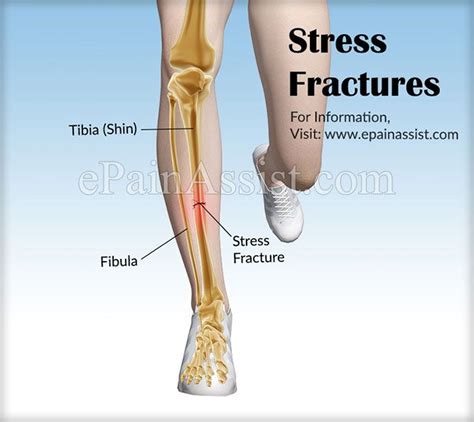
A stress fracture of the shin, also known as a tibial stress fracture, is a common overuse injury that affects the tibia, the larger of the two bones in the lower leg. This type of injury occurs when there is a small crack or fracture in the bone, typically as a result of repetitive stress or strain. Athletes and individuals who participate in high-impact activities, such as running, jumping, or dancing, are at a higher risk of developing a stress fracture of the shin.
The shin is a complex structure that consists of the tibia, fibula, and surrounding soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The tibia is the weight-bearing bone in the lower leg, and it is subjected to significant stress and strain during weight-bearing activities. When the tibia is subjected to repetitive stress, it can lead to the formation of microfractures, which can eventually coalesce to form a larger fracture. Stress fractures of the shin can be caused by a variety of factors, including overtraining, poor foot mechanics, and inadequate footwear or training surfaces.
Key Points
- Stress fractures of the shin are common overuse injuries that affect the tibia.
- Athletes and individuals who participate in high-impact activities are at a higher risk of developing a stress fracture of the shin.
- Stress fractures can be caused by a variety of factors, including overtraining, poor foot mechanics, and inadequate footwear or training surfaces.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent further injury and promote healing.
- Recovery from a stress fracture of the shin typically requires a period of rest, rehabilitation, and gradual return to activity.
Causes and Risk Factors
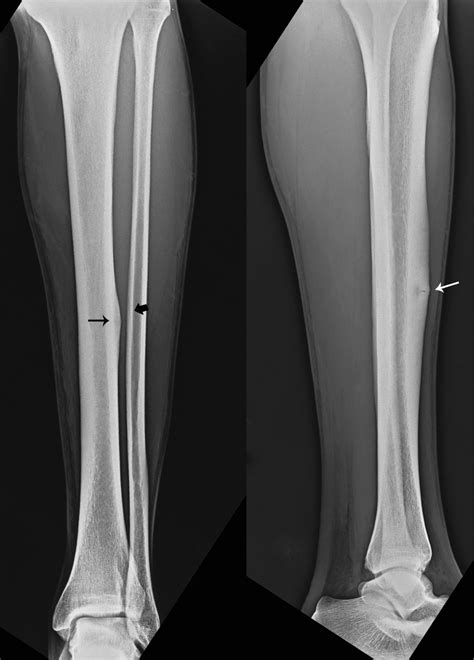
Stress fractures of the shin are often caused by a combination of factors, including overtraining, poor foot mechanics, and inadequate footwear or training surfaces. Overtraining is a common cause of stress fractures, as it can lead to repetitive stress and strain on the bones. Poor foot mechanics, such as overpronation or supination, can also contribute to the development of stress fractures, as they can alter the distribution of stress on the bones. Inadequate footwear or training surfaces can also increase the risk of stress fractures, as they can provide inadequate support or cushioning.
Athletes and individuals who participate in high-impact activities are at a higher risk of developing a stress fracture of the shin. Runners, jumpers, and dancers are particularly at risk, as they often participate in activities that involve repetitive jumping, landing, and weight-bearing. Other factors that can increase the risk of stress fractures include a history of previous stress fractures, osteoporosis, or other bone disorders, as well as certain medications or nutritional deficiencies.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of a stress fracture of the shin can vary, but they often include pain, swelling, and bruising in the affected area. The pain may be dull and aching at first, but it can become sharper and more severe over time. In some cases, the pain may be severe enough to limit activity or cause significant discomfort. A thorough medical evaluation, including a physical examination and imaging studies, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is typically necessary to diagnose a stress fracture of the shin.
| Diagnostic Test | Description |
|---|---|
| X-rays | Imaging study that uses radiation to produce images of the bones. |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Imaging study that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the bones and soft tissues. |
| Bone Scan | Imaging study that uses a small amount of radioactive material to produce images of the bones. |
| Computed Tomography (CT) Scan | Imaging study that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the bones and soft tissues. |
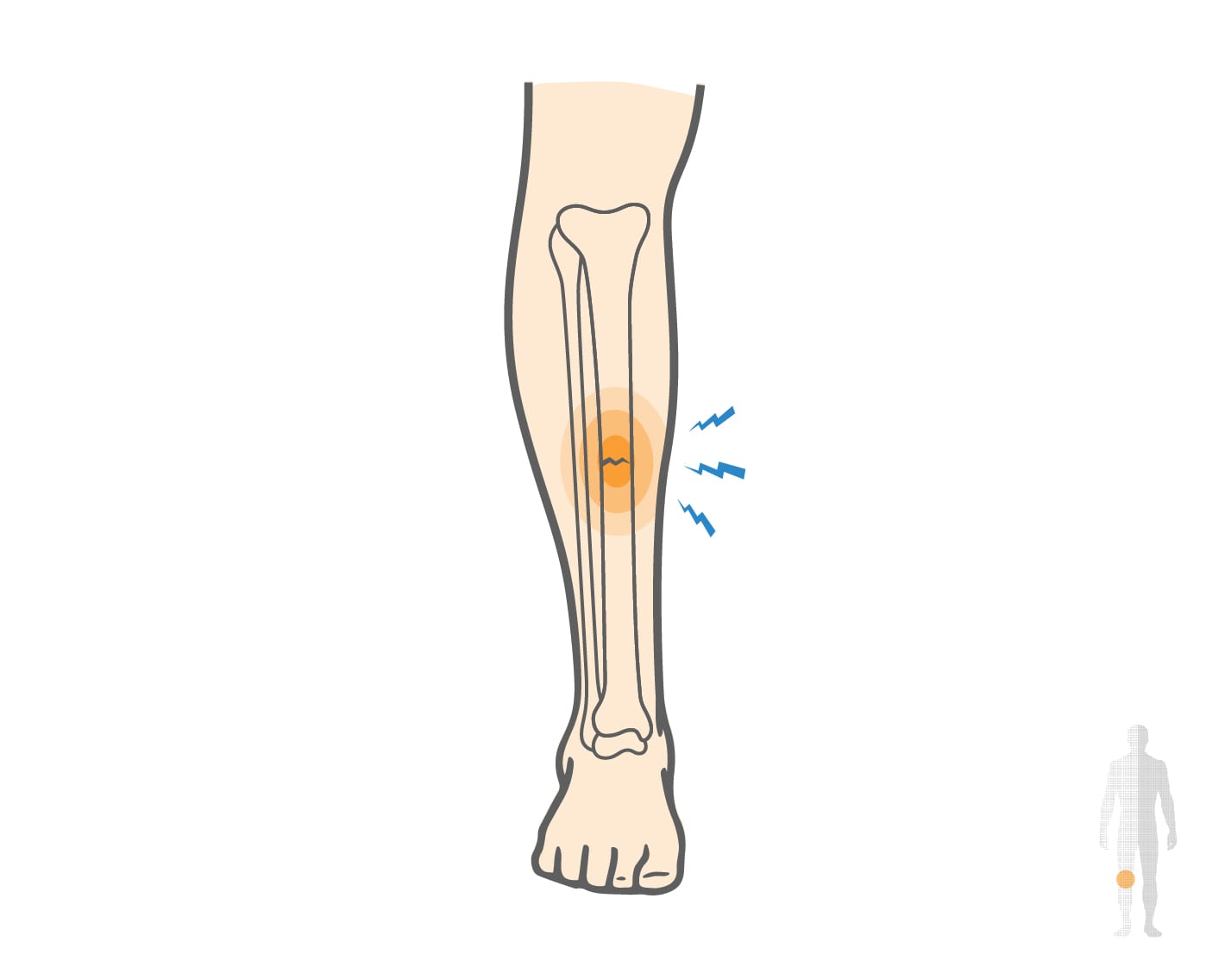
Treatment and Rehabilitation

The treatment and rehabilitation of a stress fracture of the shin typically involve a period of rest, rehabilitation, and gradual return to activity. The goal of treatment is to allow the bone to heal and to prevent further injury. A period of rest, typically 4-6 weeks, is often necessary to allow the bone to heal. During this time, it is essential to avoid activities that aggravate the condition, such as running or jumping.
Rehabilitation typically involves a gradual return to activity, starting with low-impact activities such as cycling or swimming. As the bone heals, more strenuous activities can be introduced, but it is essential to progress gradually to avoid further injury. Strengthening exercises, such as toe curls and heel raises, can also help to improve foot mechanics and reduce the risk of further injury.
Prevention
Prevention is critical to reducing the risk of stress fractures of the shin. Athletes and individuals who participate in high-impact activities can take several steps to reduce their risk, including wearing proper footwear, using orthotics or shoe inserts, and incorporating strengthening exercises into their training program. Gradually increasing training intensity and volume can also help to reduce the risk of stress fractures.
What is the most common cause of stress fractures of the shin?
+Overtraining is the most common cause of stress fractures of the shin.
How long does it take to recover from a stress fracture of the shin?
+Recovery from a stress fracture of the shin typically requires 4-6 weeks of rest and rehabilitation.
Can stress fractures of the shin be prevented?
+Yes, stress fractures of the shin can be prevented by wearing proper footwear, using orthotics or shoe inserts, and incorporating strengthening exercises into your training program.
In conclusion, stress fractures of the shin are common overuse injuries that can be caused by a variety of factors, including overtraining, poor foot mechanics, and inadequate footwear or training surfaces. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent further injury and promote healing. A thorough medical evaluation, including a physical examination and imaging studies, is typically necessary to diagnose a stress fracture of the shin. Treatment and rehabilitation involve a period of rest, rehabilitation, and gradual return to activity, with the goal of allowing the bone to heal and preventing further injury. Prevention is critical to reducing the risk of stress fractures, and athletes and individuals who participate in high-impact activities can take several steps to reduce their risk, including wearing proper footwear, using orthotics or shoe inserts, and incorporating strengthening exercises into their training program.