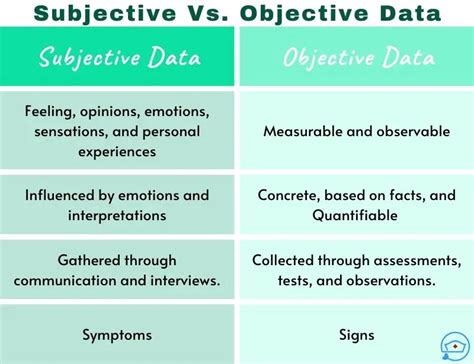
The realm of data analysis is often divided into two primary categories: subjective and objective data. Understanding the distinction between these two types of data is crucial for making informed decisions, as it directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the conclusions drawn from the data. In this article, we will delve into the world of subjective and objective data comparison, exploring the definitions, characteristics, and implications of each, as well as providing practical examples and case studies to illustrate their applications.
Introduction to Subjective and Objective Data

Subjective data refers to information that is influenced by personal opinions, emotions, or biases. This type of data is often collected through surveys, interviews, or focus groups, where respondents provide their individual perspectives or experiences. On the other hand, objective data is characterized by its independence from personal feelings or opinions, relying on factual information and empirical evidence. Examples of objective data include numerical values, scientific measurements, and statistical analysis.
Key Points
- Subjective data is influenced by personal opinions and biases, while objective data is based on factual information and empirical evidence.
- The distinction between subjective and objective data is crucial for making informed decisions and drawing accurate conclusions.
- Subjective data can provide valuable insights into human experiences and behaviors, but its reliability and validity may be limited by personal biases and emotions.
- Objective data, on the other hand, offers a more reliable and generalizable representation of reality, but may not capture the complexities and nuances of human experiences.
- A balanced approach that combines both subjective and objective data can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a research topic or business problem.
Characteristics of Subjective Data
Subjective data is often characterized by its qualitative nature, which means that it is typically collected through non-numerical methods such as text, images, or observations. This type of data is highly dependent on the context in which it is collected, as well as the individuals providing the information. Subjective data can be influenced by various factors, including personal experiences, cultural background, and social environment. For instance, a survey question asking about customer satisfaction may elicit different responses based on the respondent’s individual expectations and experiences.
| Subjective Data Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|
| Qualitative nature | Text, images, observations |
| Context-dependent | Surveys, interviews, focus groups |
| Influenced by personal factors | Personal experiences, cultural background, social environment |
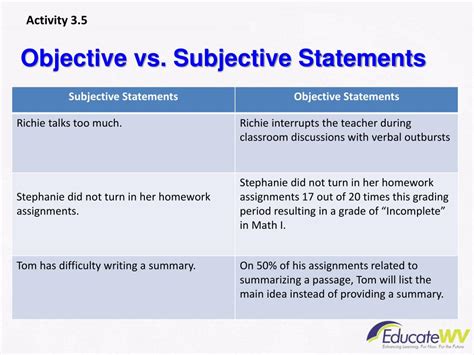
Characteristics of Objective Data
Objective data, on the other hand, is typically quantitative in nature, relying on numerical values and statistical analysis to provide insights. This type of data is often collected through systematic and structured methods, such as experiments, observations, or sensors. Objective data is less susceptible to personal biases and emotions, as it is based on empirical evidence and factual information. For example, a study on the effects of climate change may use objective data such as temperature readings, sea level measurements, and carbon dioxide levels to support its conclusions.
| Objective Data Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|
| Quantitative nature | Numerical values, statistical analysis |
| Systematic and structured collection | Experiments, observations, sensors |
| Empirical evidence-based | Temperature readings, sea level measurements, carbon dioxide levels |
Comparison of Subjective and Objective Data

A comparison of subjective and objective data reveals distinct differences in their characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Subjective data provides valuable insights into human experiences and behaviors, but its reliability and validity may be limited by personal biases and emotions. Objective data, on the other hand, offers a more reliable and generalizable representation of reality, but may not capture the complexities and nuances of human experiences. A balanced approach that combines both subjective and objective data can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a research topic or business problem.
Implications of Subjective and Objective Data
The implications of subjective and objective data are far-reaching, with significant consequences for decision-making, policy development, and business strategy. Subjective data can inform marketing campaigns, product development, and customer service initiatives, while objective data can guide investment decisions, risk assessment, and operational optimization. However, it is essential to consider the limitations and potential biases of each type of data, as well as the context in which it is collected and analyzed.
For instance, a company may use subjective data from customer surveys to inform its marketing strategy, but it is essential to consider the potential biases and limitations of this data. On the other hand, a company may use objective data from financial reports to guide its investment decisions, but it is essential to consider the context in which this data is collected and analyzed.
What is the primary difference between subjective and objective data?
+The primary difference between subjective and objective data is that subjective data is influenced by personal opinions and biases, while objective data is based on factual information and empirical evidence.
How can subjective data be used in decision-making?
+Subjective data can be used in decision-making to inform marketing campaigns, product development, and customer service initiatives. However, it is essential to consider the potential biases and limitations of this type of data.
What are the implications of objective data in business strategy?
+Objective data can guide investment decisions, risk assessment, and operational optimization. However, it is essential to consider the context in which this data is collected and analyzed, as well as the potential limitations and biases of the data.
In conclusion, the comparison of subjective and objective data highlights the importance of considering the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each type of data. By understanding the differences between subjective and objective data, researchers and analysts can develop a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of their research topic or business problem. A balanced approach that combines both subjective and objective data can provide a more accurate and reliable representation of reality, ultimately informing better decision-making and strategic planning.
Meta Description: Learn about the differences between subjective and objective data, including their characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Discover how to balance these types of data for more accurate and reliable decision-making. (145 characters)