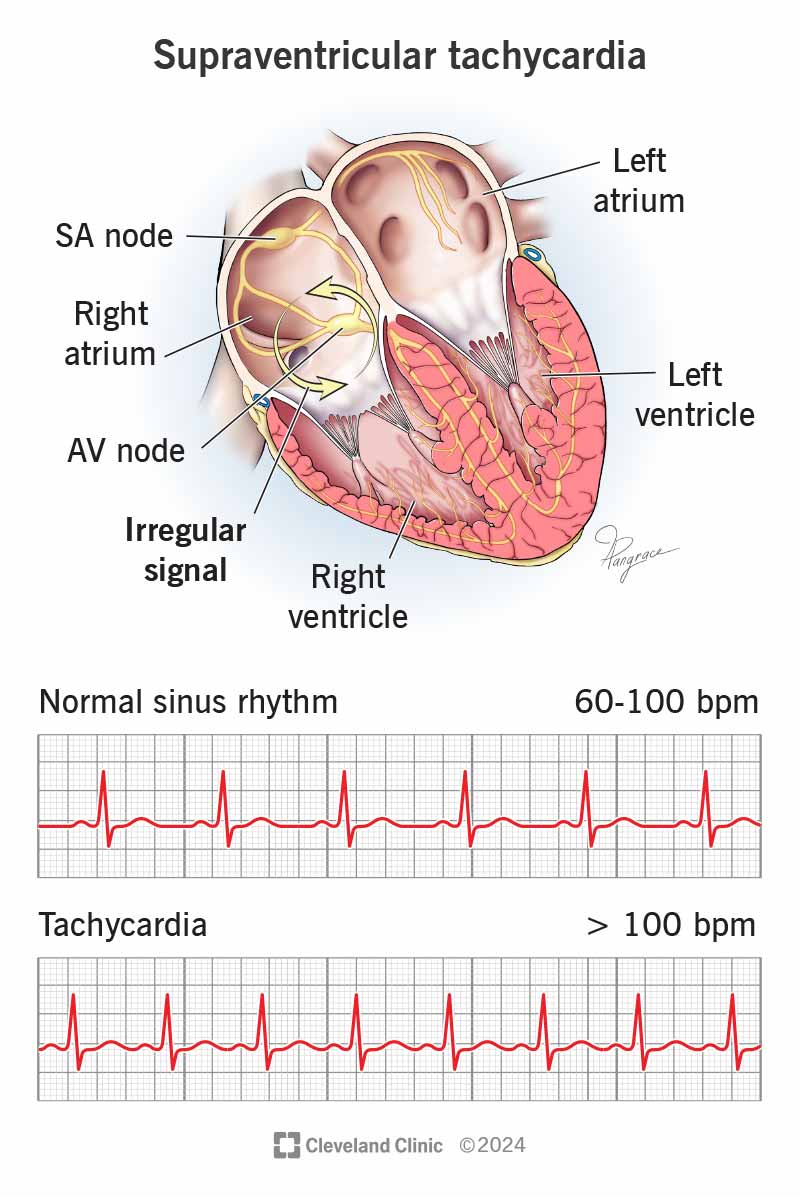
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate that originates from a location above the ventricles in the heart. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including abnormal electrical pathways in the heart, stress, caffeine, and certain medications. SVT is typically diagnosed using an electrocardiogram (ECG), which measures the electrical activity of the heart. Treatment options for SVT depend on the severity of the condition and may include vagal maneuvers, medication, and medical procedures such as cardioversion and catheter ablation.
The primary goal of treating SVT is to restore a normal heart rhythm and alleviate symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness. In some cases, SVT may resolve on its own without treatment, but in other cases, medical intervention is necessary to prevent complications such as heart failure or stroke. A comprehensive treatment plan for SVT typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and medical procedures. Lifestyle modifications may include reducing stress, avoiding triggers such as caffeine and nicotine, and getting regular exercise. Medications such as beta blockers and calcium channel blockers may be prescribed to slow the heart rate and prevent episodes of SVT.
Key Points
- SVT is a condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate that originates from a location above the ventricles in the heart.
- Treatment options for SVT depend on the severity of the condition and may include vagal maneuvers, medication, and medical procedures such as cardioversion and catheter ablation.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as reducing stress and avoiding triggers, can help prevent episodes of SVT.
- Medications such as beta blockers and calcium channel blockers may be prescribed to slow the heart rate and prevent episodes of SVT.
- Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to destroy the abnormal electrical pathway in the heart.
Treatment Options for Supraventricular Tachycardia

Treatment options for SVT vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Vagal maneuvers, such as the Valsalva maneuver or the carotid massage, may be used to try to restore a normal heart rhythm. These maneuvers work by stimulating the vagus nerve, which can help slow the heart rate. If vagal maneuvers are unsuccessful, medication may be prescribed to slow the heart rate and prevent episodes of SVT. In some cases, cardioversion may be necessary to restore a normal heart rhythm. Cardioversion involves the use of electrical shocks to convert an abnormal heart rhythm back to a normal rhythm.
Catheter Ablation for Supraventricular Tachycardia
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to destroy the abnormal electrical pathway in the heart. This procedure is typically used to treat SVT that is caused by an accessory electrical pathway in the heart. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted through a vein in the leg and guided to the heart using X-ray imaging. Once the catheter is in place, radiofrequency energy is used to destroy the abnormal electrical pathway. Catheter ablation is a highly effective treatment for SVT, with success rates ranging from 90-95%. However, the procedure is not without risks, and potential complications include bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or surrounding tissues.
| Treatment Option | Description | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Vagal Maneuvers | Stimulate the vagus nerve to slow the heart rate | 50-70% |
| Medication | Slow the heart rate and prevent episodes of SVT | 70-90% |
| Cardioversion | Use electrical shocks to convert an abnormal heart rhythm back to a normal rhythm | 90-95% |
| Catheter Ablation | Use radiofrequency energy to destroy the abnormal electrical pathway in the heart | 90-95% |
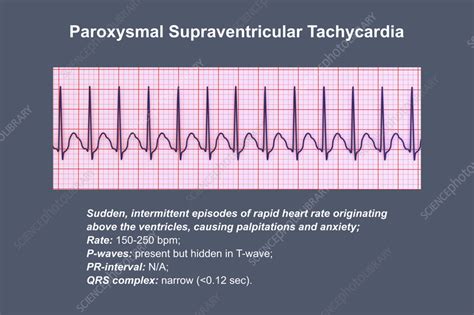
Risks and Complications of Supraventricular Tachycardia Treatment
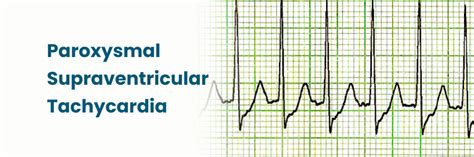
While treatment for SVT is generally safe and effective, there are potential risks and complications that can occur. These may include bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or surrounding tissues. In rare cases, treatment for SVT can also cause complications such as heart failure, stroke, or cardiac arrest. It is essential to discuss the potential risks and complications of treatment with a healthcare provider before undergoing any medical procedure.
Prevention of Supraventricular Tachycardia
While it is not possible to prevent all cases of SVT, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These may include reducing stress, avoiding triggers such as caffeine and nicotine, and getting regular exercise. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and managing underlying medical conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes can also help reduce the risk of developing SVT.
What is the most effective treatment for supraventricular tachycardia?
+The most effective treatment for SVT depends on the individual's overall health, the severity of the condition, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions. A comprehensive treatment plan that takes into account the individual's unique needs and circumstances is essential for achieving the best possible outcomes.
What are the risks and complications of catheter ablation for supraventricular tachycardia?
+The risks and complications of catheter ablation for SVT include bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or surrounding tissues. In rare cases, the procedure can also cause complications such as heart failure, stroke, or cardiac arrest.
Can supraventricular tachycardia be prevented?
+While it is not possible to prevent all cases of SVT, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These may include reducing stress, avoiding triggers such as caffeine and nicotine, and getting regular exercise. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and managing underlying medical conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes can also help reduce the risk of developing SVT.
In conclusion, supraventricular tachycardia is a condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications and restore a normal heart rhythm. Treatment options for SVT vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health, and may include vagal maneuvers, medication, and medical procedures such as cardioversion and catheter ablation. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for SVT, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing the condition and achieve the best possible outcomes.
Meta Description: Learn about supraventricular tachycardia, a condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate, and discover treatment options, including vagal maneuvers, medication, and medical procedures such as cardioversion and catheter ablation.