Svt, or supraventricular tachycardia, is a condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate that originates from a location above the ventricles. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, certain medications, and underlying heart conditions. When it comes to managing Svt, medication plays a crucial role in regulating the heart rate and preventing episodes of tachycardia. In this article, we will delve into the different types of medications used to treat Svt, their mechanisms of action, and the potential benefits and risks associated with each.
Key Points
- Adenosine is a commonly used medication for acute Svt episodes, working by slowing the heart rate and increasing the time between heartbeats.
- Calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil and diltiazem, can help regulate the heart rate and reduce the frequency of Svt episodes.
- Beta blockers, including metoprolol and atenolol, are often used to manage Svt by reducing the heart rate and decreasing the force of contractions.
- Anti-arrhythmic medications, such as flecainide and propafenone, can be used to prevent Svt episodes, but may have potential side effects and interactions.
- Lifestyle modifications, including stress reduction and avoidance of triggers, can complement medication therapy and help manage Svt symptoms.
Medications for Acute Svt Episodes
For acute episodes of Svt, medications that can quickly slow the heart rate and convert it back to a normal rhythm are essential. Adenosine is a medication that is commonly used in this setting, as it has a rapid onset of action and can effectively terminate Svt episodes in many cases. Adenosine works by activating potassium channels in the heart, which slows the heart rate and increases the time between heartbeats. This allows the heart to reset and return to a normal rhythm.
Calcium Channel Blockers and Beta Blockers
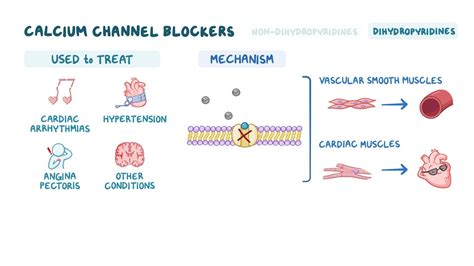
Calcium channel blockers and beta blockers are two classes of medications that are often used to manage Svt. Calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil and diltiazem, work by blocking the influx of calcium ions into the heart cells, which helps to slow the heart rate and reduce the force of contractions. Beta blockers, including metoprolol and atenolol, decrease the heart rate and reduce the force of contractions by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart. Both of these classes of medications can be effective in managing Svt, but may have potential side effects, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue.
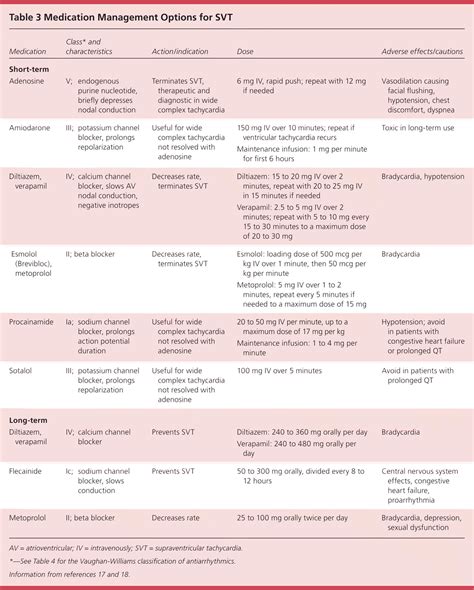
| Medication Class | Examples | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium Channel Blockers | Verapamil, Diltiazem | Block calcium influx into heart cells |
| Beta Blockers | Metoprolol, Atenolol | Block effects of adrenaline on the heart |
| Anti-arrhythmic Medications | Flecainide, Propafenone | Block abnormal electrical pathways in the heart |
Long-term Management of Svt
For individuals who experience recurrent Svt episodes, long-term management is crucial to prevent complications and improve quality of life. Anti-arrhythmic medications, such as flecainide and propafenone, can be used to prevent Svt episodes, but may have potential side effects and interactions. These medications work by blocking abnormal electrical pathways in the heart, which can help to prevent Svt episodes. However, they may require regular monitoring and dose adjustments to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Lifestyle Modifications and Svt Management
In addition to medication therapy, lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing Svt symptoms. Avoiding triggers, such as stress and certain medications, can help to reduce the frequency of Svt episodes. Engaging in regular physical activity, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and getting adequate sleep can also help to improve overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of complications. By combining medication therapy with lifestyle modifications, individuals with Svt can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
What are the most common medications used to treat Svt?
+The most common medications used to treat Svt include adenosine, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, and anti-arrhythmic medications. The specific medication used will depend on individual factors, such as the underlying cause of the condition and medical history.
Can lifestyle modifications help manage Svt symptoms?
+Yes, lifestyle modifications can help manage Svt symptoms. Avoiding triggers, engaging in regular physical activity, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and getting adequate sleep can all help to improve overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of complications.
What are the potential risks and benefits of medication therapy for Svt?
+The potential risks and benefits of medication therapy for Svt will depend on the specific medication used and individual factors, such as medical history and lifestyle. It's essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the different types of medications used to treat Svt, including adenosine, calcium channel blockers, and beta blockers, and learn how lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.” (149 characters)
Related Terms:
- Adenosine
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- svt medication
- SVT emergency treatment
- Supraventricular tachycardia medication list
- How to stop SVT attack