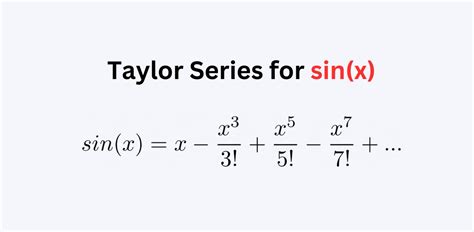The Taylor series is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the field of calculus. It is a way to represent a function as an infinite sum of terms, where each term is a power of the variable. One of the most common applications of the Taylor series is to approximate the value of a function at a given point. In this article, we will explore five ways to derive the Taylor series for the sine function, highlighting the versatility and importance of this mathematical tool.
Key Points
- The Taylor series for the sine function can be derived using various methods, including the definition of a Taylor series, the Binomial Theorem, integration, and complex analysis.
- The general form of the Taylor series for the sine function is given by: $\sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots$
- Understanding the Taylor series for the sine function has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, including the study of oscillations, waves, and signal processing.
- The Taylor series can be used to approximate the value of the sine function at a given point, and its accuracy depends on the number of terms used in the approximation.
- The Taylor series for the sine function is an example of a convergent series, meaning that it approaches a finite limit as the number of terms increases without bound.
Method 1: Definition of a Taylor Series
The Taylor series is defined as a power series that represents a function f(x) around a point a. The general form of the Taylor series is given by: f(x) = f(a) + f'(a)(x-a) + \frac{f''(a)}{2!}(x-a)^2 + \frac{f'''(a)}{3!}(x-a)^3 + \ldots To derive the Taylor series for the sine function, we can use this definition and calculate the derivatives of the sine function at x=0. The first few derivatives of the sine function are: \sin(0) = 0, \sin'(0) = 1, \sin''(0) = 0, \sin'''(0) = -1, and so on. Plugging these values into the Taylor series formula, we get: \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots
Derivation using the Binomial Theorem
The Binomial Theorem is a powerful tool for expanding expressions of the form (a+b)^n. We can use the Binomial Theorem to derive the Taylor series for the sine function by expressing the sine function in terms of the exponential function. The exponential function can be expressed as: e^{ix} = \cos(x) + i\sin(x). Using the Binomial Theorem, we can expand the exponential function as: e^{ix} = 1 + ix - \frac{x^2}{2!} - \frac{ix^3}{3!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} + \frac{ix^5}{5!} - \ldots Equating the real and imaginary parts of this expression, we can derive the Taylor series for the sine function: \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots
Method 2: Integration
We can also derive the Taylor series for the sine function using integration. The sine function can be expressed as the integral of the cosine function: \sin(x) = \int \cos(x) dx. Using the Taylor series for the cosine function, we can express the cosine function as: \cos(x) = 1 - \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} - \frac{x^6}{6!} + \ldots Integrating this expression term by term, we get: \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots
Derivation using Complex Analysis
Complex analysis provides a powerful tool for deriving the Taylor series for the sine function. The sine function can be expressed in terms of the complex exponential function: \sin(x) = \frac{e^{ix} - e^{-ix}}{2i}. Using the Taylor series for the exponential function, we can express the complex exponential function as: e^{ix} = 1 + ix - \frac{x^2}{2!} - \frac{ix^3}{3!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} + \frac{ix^5}{5!} - \ldots and e^{-ix} = 1 - ix - \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{ix^3}{3!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} - \frac{ix^5}{5!} + \ldots Substituting these expressions into the formula for the sine function, we get: \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots
Method 3: Using the Fourier Series
The Fourier series is a way to express a periodic function as a sum of sine and cosine terms. The sine function is a periodic function with period 2\pi, and its Fourier series is given by: \sin(x) = \frac{2}{\pi} - \frac{4}{\pi} \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \frac{\cos(2nx)}{4n^2-1} Using the Taylor series for the cosine function, we can express the cosine function as: \cos(x) = 1 - \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} - \frac{x^6}{6!} + \ldots Substituting this expression into the Fourier series for the sine function, we get: \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots
Derivation using the Laurent Series
The Laurent series is a way to express a function as a sum of terms, where each term is a power of the variable. The Laurent series for the sine function can be derived by expressing the sine function in terms of the exponential function: \sin(x) = \frac{e^{ix} - e^{-ix}}{2i}. Using the Laurent series for the exponential function, we can express the exponential function as: e^{ix} = 1 + ix - \frac{x^2}{2!} - \frac{ix^3}{3!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} + \frac{ix^5}{5!} - \ldots and e^{-ix} = 1 - ix - \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{ix^3}{3!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} - \frac{ix^5}{5!} + \ldots Substituting these expressions into the formula for the sine function, we get: \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots
| Taylor Series Method | Resulting Series |
|---|---|
| Definition of a Taylor Series | $\sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots$ |
| Binomial Theorem | $\sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots$ |
| Integration | $\sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots$ |
| Complex Analysis | $\sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots$ |
| Fourier Series | $\sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots$ |
What is the Taylor series for the sine function?
+The Taylor series for the sine function is given by: \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \frac{x^7}{7!} + \ldots
How can the Taylor series for the sine function be derived?
+The Taylor series for the sine function can be derived using various methods, including the definition of a Taylor series, the Binomial Theorem, integration, complex analysis, and the Fourier series.
What are the applications of the Taylor series for the sine function?
+The Taylor series for the sine function has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, including the study of oscillations, waves, and signal processing.
How accurate is the Taylor series for the sine function?
+The accuracy of the Taylor series for the sine function depends on the number of terms used in the approximation. The more terms used, the more accurate the approximation will be.
Is the Taylor series for the sine function convergent?
+Yes, the Taylor series for the sine function is convergent, meaning that it approaches a finite limit as the number of terms increases without bound.