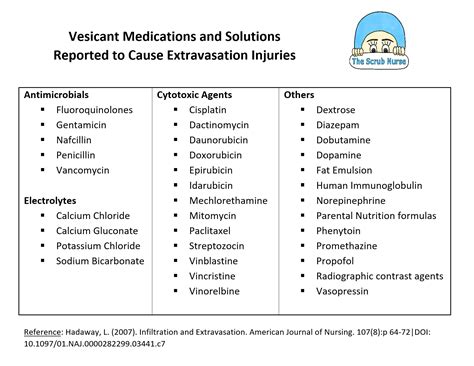
Vesicant medication, also known as vesicant agents or alkylating agents, are a class of drugs used in chemotherapy to treat various types of cancer. These medications work by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, thereby preventing them from reproducing and eventually leading to cell death. Vesicants are known for their ability to cause severe tissue damage, particularly to the skin and mucous membranes, which can result in painful blisters, ulcers, and scarring.
The term "vesicant" comes from the Latin word "vesica," meaning bladder, and refers to the ability of these agents to cause blisters or vesicles on the skin. Vesicant medications are highly potent and require careful handling and administration to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Healthcare professionals who handle these medications must take precautions to avoid skin contact and wear protective clothing, including gloves and gowns.
Key Points
- Vesicant medications are used in chemotherapy to treat various types of cancer.
- These medications work by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from reproducing.
- Vesicants can cause severe tissue damage, particularly to the skin and mucous membranes.
- Handling and administration of vesicant medications require careful precautions to minimize adverse effects.
- Healthcare professionals must take precautions to avoid skin contact and wear protective clothing when handling vesicant medications.
Types of Vesicant Medications

There are several types of vesicant medications used in chemotherapy, including:
- Mustard agents, such as mechlorethamine and melphalan, which are used to treat lymphoma, leukemia, and other types of cancer.
- Nitrogen mustards, such as cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide, which are used to treat a variety of cancers, including breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and lung cancer.
- Alkylating agents, such as busulfan and chlorambucil, which are used to treat chronic myeloid leukemia and other types of cancer.
Administration and Handling of Vesicant Medications
Vesicant medications are typically administered intravenously, and handling and administration require careful precautions to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Healthcare professionals must wear protective clothing, including gloves and gowns, and use specialized equipment to administer these medications.
The administration of vesicant medications is typically done in a controlled environment, such as a hospital or clinic, where emergency equipment and personnel are available in case of an adverse reaction. Patients receiving vesicant medications are closely monitored for signs of adverse effects, such as skin irritation, blisters, or respiratory problems.
| Medication | Indication | Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Mechlorethamine | Lymphoma, leukemia | Intravenous |
| Cyclophosphamide | Breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer | Intravenous |
| Busulfan | Chronic myeloid leukemia | Oral |
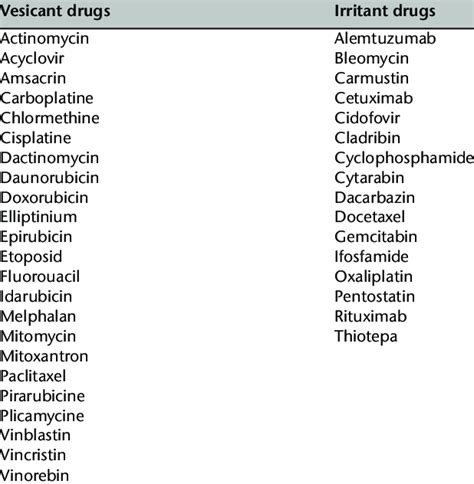
Adverse Effects of Vesicant Medications

Vesicant medications can cause a range of adverse effects, including:
- Skin irritation and blisters, which can be severe and painful.
- Mucositis, which is inflammation of the mucous membranes, particularly in the mouth and throat.
- Respiratory problems, such as coughing and shortness of breath.
- Gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
These adverse effects can be managed with supportive care, such as pain management, wound care, and nutritional support. In some cases, the administration of vesicant medications may need to be delayed or discontinued due to severe adverse effects.
Management of Adverse Effects
The management of adverse effects associated with vesicant medications requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving healthcare professionals from various specialties, including oncology, nursing, and pharmacy.
Patient education is essential in managing adverse effects, and patients should be informed about the potential risks and benefits of vesicant medications. Patients should also be taught how to manage adverse effects, such as skin irritation and mucositis, and when to seek medical attention.
What are vesicant medications used for?
+Vesicant medications are used in chemotherapy to treat various types of cancer, including lymphoma, leukemia, and breast cancer.
How are vesicant medications administered?
+Vesicant medications are typically administered intravenously, and handling and administration require careful precautions to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
What are the potential adverse effects of vesicant medications?
+Vesicant medications can cause a range of adverse effects, including skin irritation, mucositis, respiratory problems, and gastrointestinal problems.