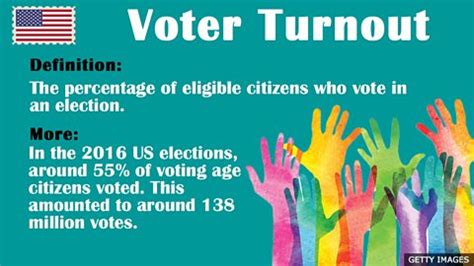
Voter turnout is a crucial aspect of democratic processes, reflecting the percentage of eligible citizens who participate in elections by casting their ballots. It is a key indicator of the health of a democracy, as high turnout rates suggest that citizens are engaged and invested in the political process, while low turnout can indicate disillusionment or a lack of faith in the system. The meaning of voter turnout extends beyond mere numbers, as it encompasses the principles of representation, legitimacy, and the overall quality of governance. Understanding voter turnout requires examining its various dimensions, including the factors that influence it, such as socio-economic status, education level, and the accessibility of voting processes.
The significance of voter turnout can be understood through its implications on policy making and political representation. When a significant portion of the electorate participates in voting, the government is more likely to reflect the will of the people, leading to policies that are more representative of the broader population's interests. Conversely, low voter turnout can result in governments that do not fully represent the diverse views and needs of their citizens, potentially leading to policies that benefit specific groups at the expense of others. Thus, voter turnout is not just a statistical measure but a vital component of democratic functioning and accountability.
Key Points
- Voter turnout is a measure of the percentage of eligible voters who cast ballots in an election.
- High voter turnout is generally seen as indicative of a healthy democracy, where citizens are engaged and believe their votes matter.
- Low voter turnout can suggest disillusionment with the political process or barriers to voting, such as restrictive voting laws or lack of access to polling stations.
- Voter turnout affects the legitimacy and representation of governments, with higher turnout potentially leading to more inclusive and responsive policy-making.
- Factors influencing voter turnout include socio-economic status, education level, voting laws, and the competitiveness of elections.
Factors Influencing Voter Turnout
Several factors contribute to voter turnout, including demographic characteristics of the electorate, the legal and regulatory framework governing voting, and the nature of political campaigns and competitions. Socio-economic status and education level are significant predictors of voter turnout, with higher levels of income and education generally associated with higher rates of voting. The accessibility of voting processes, including the ease of registration, the availability of early or mail-in voting options, and the location and hours of polling stations, also plays a critical role. In addition, the competitiveness of elections and the perceived impact of one’s vote can significantly influence an individual’s decision to participate in the electoral process.
The Role of Voting Laws and Regulations
Voting laws and regulations can either facilitate or hinder voter turnout. Laws that simplify voter registration, extend early voting periods, and allow for mail-in ballots can increase participation by making voting more convenient and accessible. On the other hand, laws that impose strict voter ID requirements, limit early voting, or purge voter rolls can reduce turnout, particularly among certain demographic groups such as the poor, minorities, and the elderly, who may face greater barriers to obtaining necessary documents or accessing polling places. The impact of these laws underscores the importance of voting rights and access in determining voter turnout rates.
| Factor | Influence on Voter Turnout |
|---|---|
| Socio-economic Status | Higher income and education levels are associated with higher voter turnout. |
| Voting Laws and Accessibility | Laws and practices that make voting easier and more accessible tend to increase turnout, while restrictive laws can decrease it. |
| Competitiveness of Elections | Electoral competitions perceived as close or significant can boost voter turnout. |
| Political Engagement and Mobilization | Efforts by political parties, campaigns, and community organizations to mobilize voters can increase turnout. |
Improving Voter Turnout
Strategies to improve voter turnout are multifaceted and include both short-term and long-term approaches. In the short term, political campaigns and community organizations can engage in voter mobilization efforts, such as get-out-the-vote campaigns, voter registration drives, and educational programs aimed at informing citizens about the voting process and the importance of their participation. Long-term strategies involve structural reforms, such as automatic voter registration, expansion of early and mail-in voting, and the implementation of voting holiday policies to make Election Day a national holiday, thereby increasing accessibility and reducing barriers to voting.
Technology and Voter Engagement
The integration of technology into the electoral process presents both opportunities and challenges for improving voter turnout. Online voter registration platforms, digital voter guides, and social media campaigns can increase awareness and engagement among potential voters, particularly younger demographics. However, the digital divide and concerns about election security must be addressed to ensure that technological innovations enhance, rather than hinder, democratic participation.
In conclusion, voter turnout is a critical metric of democratic health, influenced by a complex array of factors including socio-economic status, voting laws, political engagement, and technological accessibility. Understanding these factors and implementing strategies to address them is essential for fostering a more inclusive and participatory democracy. By promoting higher voter turnout, societies can work towards governments that are more representative and responsive to the needs and interests of all citizens.
What is the significance of voter turnout in a democracy?
+Voter turnout is significant because it reflects the level of citizen engagement and participation in the democratic process. High turnout rates indicate that citizens feel their votes matter and are invested in the outcome of elections, which can lead to more representative and accountable government.
How do voting laws and regulations affect voter turnout?
+Voting laws and regulations can significantly impact voter turnout. Laws that make voting more accessible, such as online registration and early voting, can increase turnout, while restrictive laws, such as strict ID requirements, can decrease it, particularly among certain demographic groups.
What strategies can be used to improve voter turnout?
+Strategies to improve voter turnout include voter mobilization efforts, structural reforms like automatic voter registration and voting holiday policies, and the use of technology to increase accessibility and engagement. Educational programs and community outreach are also crucial for informing citizens about the voting process and the importance of their participation.