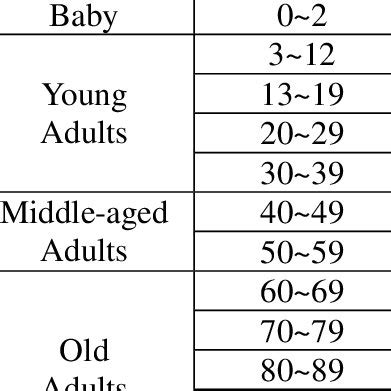
The concept of "Young Adult Age" is a term that refers to the life stage between adolescence and adulthood, typically spanning from the late teens to the late twenties. This period is characterized by significant physical, emotional, social, and psychological changes, as individuals transition from dependence on their families to independence and self-sufficiency.
Defining Young Adulthood
Young adulthood is generally defined as the period between 18 and 29 years of age, although the exact boundaries may vary depending on cultural, social, and economic contexts. During this stage, individuals typically experience a range of developmental milestones, including completing education, entering the workforce, forming romantic relationships, and developing their own identities.
Physical and Emotional Development
Young adults undergo significant physical changes, such as the completion of physical growth and the development of adult physical characteristics. Emotionally, they may experience increased emotional regulation, improved impulse control, and enhanced self-awareness. However, this stage is also marked by potential challenges, such as navigating social relationships, managing stress and anxiety, and coping with uncertainty and ambiguity.
| Age Range | Developmental Milestones |
|---|---|
| 18-22 years | Completing high school, entering higher education, developing social networks |
| 23-26 years | Entering the workforce, forming romantic relationships, developing emotional regulation |
| 27-29 years | Establishing career stability, forming long-term relationships, developing financial independence |
Young adulthood is also a time of exploration and experimentation, as individuals try out different roles, identities, and lifestyles. This stage is marked by a sense of freedom and autonomy, as well as increased responsibility and accountability.
Social and Cultural Contexts

The experience of young adulthood varies significantly across different cultural, social, and economic contexts. In some societies, young adults may be expected to take on significant family responsibilities, while in others, they may be encouraged to pursue individual goals and aspirations.
Economic and Educational Factors
Young adults from disadvantaged backgrounds may face significant barriers to education and employment, while those from more affluent backgrounds may have greater access to resources and opportunities. Education and economic stability are critical factors that can influence the trajectory of young adulthood, with significant implications for long-term health, well-being, and life satisfaction.
Key Points
- Young adulthood is a critical period for physical, emotional, and social development.
- The experience of young adulthood varies across different cultural, social, and economic contexts.
- Education and economic stability are critical factors that can influence the trajectory of young adulthood.
- Young adults face significant challenges, including navigating social relationships, managing stress and anxiety, and coping with uncertainty and ambiguity.
- Establishing healthy habits, developing emotional resilience, and forming meaningful relationships are essential for long-term well-being.
In conclusion, young adulthood is a complex and multifaceted stage of life, marked by significant developmental milestones, challenges, and opportunities. By understanding the physical, emotional, social, and cultural contexts of young adulthood, we can better support the health, well-being, and success of young adults as they navigate this critical life stage.
What are the key challenges faced by young adults?
+Young adults face a range of challenges, including navigating social relationships, managing stress and anxiety, coping with uncertainty and ambiguity, and establishing financial independence.
How can young adults develop emotional resilience?
+Young adults can develop emotional resilience by practicing self-care, building social support networks, engaging in physical activity, and developing healthy coping mechanisms, such as mindfulness and stress management techniques.
What role do education and economic stability play in young adulthood?
+Education and economic stability are critical factors that can influence the trajectory of young adulthood, with significant implications for long-term health, well-being, and life satisfaction. Access to education and employment opportunities can provide young adults with the skills, knowledge, and resources needed to establish financial independence and pursue their goals and aspirations.