Footnotes are a crucial element in academic and professional writing, serving as a means to provide additional information, clarify complex concepts, and acknowledge sources without interrupting the flow of the main text. They are typically denoted by a superscript number or symbol in the text, which corresponds to a footnote at the bottom of the page or at the end of the document. Footnotes can be used to provide a range of information, including:
Types of Footnotes

There are several types of footnotes, each with its own specific purpose. These include:
- Explanatory footnotes: These provide additional information or clarification on a point made in the text.
- Citation footnotes: These acknowledge the source of a quote, idea, or piece of information used in the text.
- Reference footnotes: These provide a list of sources used in the research or writing of the document.
Footnote Structure
A footnote typically consists of a superscript number or symbol in the text, which corresponds to a footnote at the bottom of the page or at the end of the document. The footnote itself usually includes the following elements:
- Footnote number or symbol: This is the superscript number or symbol that appears in the text.
- Footnote text: This is the additional information or clarification provided by the footnote.
| Footnote Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Footnote number or symbol | Superscript number or symbol in the text |
| Footnote text | Additional information or clarification provided by the footnote |
Footnotes can be presented in various formats, including:
- Endnotes: These are footnotes that are collected at the end of the document, rather than at the bottom of each page.
- Sidebar footnotes: These are footnotes that are presented in a sidebar or margin, rather than at the bottom of the page.
Best Practices for Using Footnotes
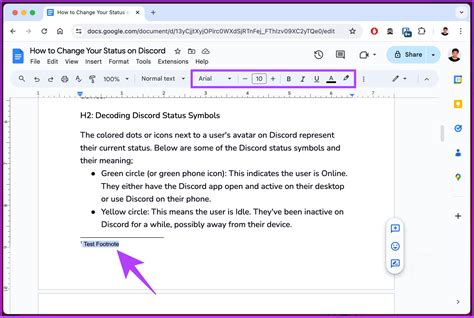
When using footnotes, it's essential to follow best practices to ensure that they are used effectively and do not disrupt the flow of the text. These include:
- Use footnotes sparingly: Footnotes should be used only when necessary to provide additional information or clarification.
- Keep footnotes concise: Footnotes should be brief and to the point, avoiding unnecessary detail or tangential information.
- Use a consistent format: Footnotes should be presented in a consistent format throughout the document, using a standard font, size, and style.
Key Points
- Footnotes provide additional information or clarification on a point made in the text.
- There are several types of footnotes, including explanatory, citation, and reference footnotes.
- Footnotes should be used judiciously and only when necessary.
- Footnotes should be concise and to the point, avoiding unnecessary detail or tangential information.
- A consistent format should be used throughout the document.
In conclusion, footnotes are a valuable tool in academic and professional writing, providing a means to provide additional information, clarify complex concepts, and acknowledge sources. By following best practices and using footnotes judiciously, writers can ensure that their footnotes are effective and do not disrupt the flow of the text.
What is the purpose of footnotes in writing?
+Footnotes provide additional information or clarification on a point made in the text, and can also be used to acknowledge sources and provide references.
How should footnotes be used in writing?
+Footnotes should be used judiciously and only when necessary to provide additional information or clarification. They should be concise and to the point, avoiding unnecessary detail or tangential information.
What are the different types of footnotes?
+There are several types of footnotes, including explanatory, citation, and reference footnotes. Explanatory footnotes provide additional information or clarification on a point made in the text, while citation footnotes acknowledge the source of a quote, idea, or piece of information used in the text. Reference footnotes provide a list of sources used in the research or writing of the document.