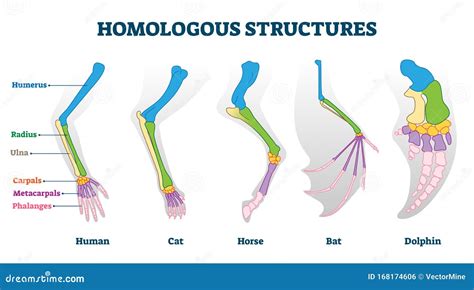
Homologous structures are a fundamental concept in biology, referring to the existence of similar structures in different species that have evolved from a common ancestor. This phenomenon is a key aspect of comparative anatomy, allowing scientists to study the evolutionary relationships between organisms and understand how different species have adapted to their environments over time. The concept of homologous structures is rooted in the idea that all living organisms share a common evolutionary history, and that their similarities and differences can be used to reconstruct their phylogenetic relationships.
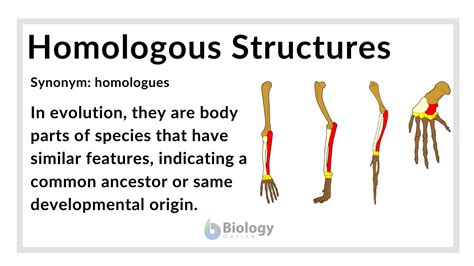
The study of homologous structures has a rich history, dating back to the early days of comparative anatomy. One of the pioneers in this field was Richard Owen, who first coined the term "homology" in the 19th century. Owen recognized that the forelimbs of vertebrates, such as the human arm, the wing of a bird, and the flipper of a whale, were all composed of the same bones, despite their different functions. This observation led him to propose that these structures were homologous, meaning that they had evolved from a common ancestral structure. Since then, the concept of homologous structures has been extensively developed and refined, with significant contributions from scientists such as Charles Darwin and Stephen Jay Gould.
Key Points
- Homologous structures are similar structures in different species that have evolved from a common ancestor.
- The concept of homologous structures is rooted in comparative anatomy and phylogenetics.
- Homologous structures can be used to study evolutionary relationships between organisms.
- The forelimbs of vertebrates are a classic example of homologous structures.
- The study of homologous structures has contributed significantly to our understanding of evolutionary biology.
Types of Homologous Structures
There are several types of homologous structures, including morphological, molecular, and developmental homologies. Morphological homologies refer to the similarity in shape and structure between different organisms, such as the similarity between the human arm and the wing of a bird. Molecular homologies, on the other hand, refer to the similarity in DNA or protein sequences between different organisms, such as the similarity between the genes that control embryonic development in different species. Developmental homologies refer to the similarity in the developmental processes that shape the formation of different structures, such as the similarity between the formation of the forelimbs in different vertebrates.
Morphological Homologies
Morphological homologies are the most visible and well-studied type of homologous structure. They can be observed in the shape and structure of different organs and tissues, such as the bones, muscles, and nerves that make up the forelimbs of vertebrates. Morphological homologies can be used to study the evolutionary relationships between different species and to reconstruct their phylogenetic history. For example, the presence of similar bones in the forelimbs of different vertebrates, such as the humerus, radius, and ulna, indicates that these structures evolved from a common ancestral structure.
| Organism | Forelimb Structure |
|---|---|
| Human | Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges |
| Bird | Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges (modified to form wing) |
| Whale | Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges (modified to form flipper) |
Evolutionary Implications

The concept of homologous structures has significant implications for our understanding of evolutionary biology. It suggests that different species have evolved from a common ancestral population, and that their similarities and differences can be used to reconstruct their phylogenetic history. The study of homologous structures has also led to a greater understanding of the mechanisms of evolution, including the role of natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow in shaping the evolution of different species.
Phylogenetic Reconstruction
Phylogenetic reconstruction is the process of using morphological, molecular, and other data to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships between different species. The study of homologous structures is a key aspect of phylogenetic reconstruction, as it allows scientists to identify the shared characteristics that indicate a common ancestral origin. By analyzing the similarities and differences between different species, scientists can reconstruct the phylogenetic tree that shows the evolutionary relationships between different organisms.
The study of homologous structures has also led to a greater understanding of the evolutionary mechanisms that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth. For example, the study of the forelimbs of vertebrates has shown that these structures have evolved to perform different functions, such as walking, flying, and swimming, despite their similar morphology. This has led to a greater understanding of the role of natural selection in shaping the evolution of different species, and has highlighted the importance of considering the functional and ecological context in which evolution occurs.
What are homologous structures?
+Homologous structures are similar structures in different species that have evolved from a common ancestor.
What are the types of homologous structures?
+There are several types of homologous structures, including morphological, molecular, and developmental homologies.
What is the significance of homologous structures in evolutionary biology?
+The study of homologous structures has significantly contributed to our understanding of evolutionary biology, allowing us to reconstruct the phylogenetic relationships between different species and to understand how they have adapted to their environments over time.
In conclusion, the concept of homologous structures is a fundamental aspect of evolutionary biology, allowing us to study the evolutionary relationships between different species and to understand how they have adapted to their environments over time. The study of homologous structures has significantly contributed to our understanding of phylogenetic reconstruction, evolutionary mechanisms, and the diversity of life on Earth. By continuing to explore and analyze homologous structures, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the complex and fascinating history of life on our planet.