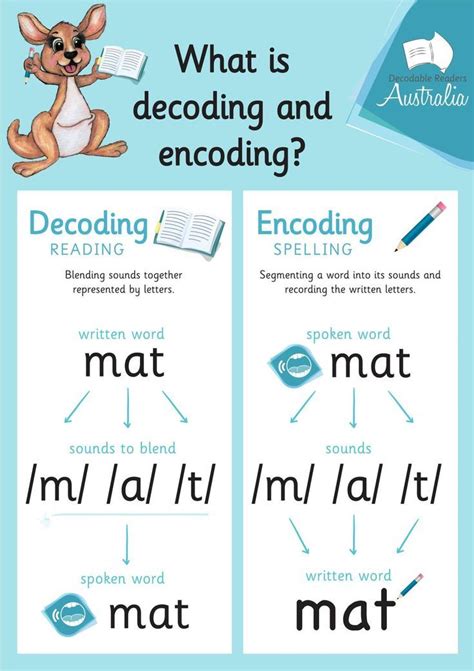
Decoding text is a fundamental aspect of understanding written communication, involving the process of translating written words into spoken language or comprehensible ideas. This skill is crucial for reading comprehension and is developed through practice and exposure to various texts. In this article, we will explore five ways to decode text, emphasizing the importance of each method in enhancing reading skills and comprehension.
Phonics-Based Decoding

Phonics-based decoding is one of the most common methods used to decode text. It involves associating sounds with letters or groups of letters, enabling readers to sound out words they have never seen before. This method is particularly effective for languages with alphabetic writing systems, such as English, where words are composed of sounds represented by letters. For instance, the word “cat” can be decoded by associating the sounds /c/, /a/, and /t/ with their respective letters. Phonics-based decoding is a foundational skill taught in early reading education, as it provides a systematic approach to reading unfamiliar words.
Advantages of Phonics-Based Decoding
The primary advantage of phonics-based decoding is its ability to help readers decode unfamiliar words independently. By understanding the relationship between sounds and letters, readers can attempt to read words they have never seen before, thus expanding their vocabulary and reading fluency. However, it’s also important to note that phonics-based decoding may not be as effective for words with irregular spellings or silent letters, where other decoding strategies might be more beneficial.
| Decoding Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Phonics-Based Decoding | Associating sounds with letters to decode words |
| Context Clues | Using surrounding text to infer word meaning |
| Sight Word Recognition | Recognizing high-frequency words by sight |
| Morphemic Analysis | Breaking down words into prefixes, roots, and suffixes |
| Semantic Mapping | Creating visual maps to connect words and ideas |

Context Clues and Sight Word Recognition

Beyond phonics-based decoding, two other significant strategies for decoding text are context clues and sight word recognition. Context clues involve using the surrounding text to infer the meaning of an unfamiliar word. This strategy relies on the reader’s ability to understand the context in which the word is used, often providing enough information to guess the word’s meaning. Sight word recognition, on the other hand, involves recognizing high-frequency words by sight, without needing to sound them out. These words are often irregular and do not follow phonetic rules, making sight recognition a necessary skill for fluent reading.
Implementing Context Clues and Sight Word Recognition
The implementation of context clues and sight word recognition in reading instruction is vital. For context clues, teachers can encourage students to read sentences or paragraphs containing unfamiliar words and then ask questions about the word’s possible meaning based on the context. For sight word recognition, educators can use flashcards, word walls, or reading games to help students memorize and recognize these words quickly. By combining these strategies with phonics-based decoding, readers can develop a robust set of skills to tackle a wide range of texts.
Key Points
- Phonics-based decoding is a foundational skill for reading that involves associating sounds with letters.
- Context clues help readers infer word meanings from surrounding text.
- Sight word recognition is crucial for high-frequency words that are irregular or do not follow phonetic rules.
- Morphemic analysis involves breaking down words into their component parts to understand their meanings.
- Semantic mapping is a visual strategy to connect words and ideas, enhancing comprehension and vocabulary.
Morphemic Analysis and Semantic Mapping
Morphemic analysis and semantic mapping are two advanced strategies for decoding and comprehending text. Morphemic analysis involves breaking down words into their component parts, such as prefixes, roots, and suffixes, to understand their meanings. This strategy is particularly useful for decoding unfamiliar words, as many words in the English language share common roots and prefixes. Semantic mapping, on the other hand, is a visual strategy that involves creating maps to connect words and ideas, thereby enhancing comprehension and vocabulary. By visually organizing information, readers can better understand relationships between concepts and retain information more effectively.
Applying Morphemic Analysis and Semantic Mapping
The application of morphemic analysis and semantic mapping in reading comprehension can significantly enhance a reader’s ability to decode and understand complex texts. For morphemic analysis, readers can start by identifying common prefixes and suffixes and their meanings, then practice breaking down words into their morphemic components. For semantic mapping, readers can begin with simple concepts, creating visual maps that connect ideas, and gradually move to more complex texts. These strategies, combined with phonics-based decoding, context clues, and sight word recognition, provide a comprehensive approach to reading and comprehension.
What is the most effective way to decode unfamiliar words?
+The most effective way to decode unfamiliar words involves a combination of strategies, including phonics-based decoding, context clues, sight word recognition, morphemic analysis, and semantic mapping. Each strategy has its strengths and is suited to different types of words and reading contexts.
How can I improve my reading comprehension?
+Improving reading comprehension involves practicing a variety of decoding strategies, reading widely, and engaging actively with texts. This includes using context clues, recognizing sight words, applying morphemic analysis, and creating semantic maps to connect ideas and concepts.
What role does vocabulary play in decoding text?
+Vocabulary plays a crucial role in decoding text, as knowing the meanings of words is essential for comprehension. Strategies like morphemic analysis and semantic mapping can help readers expand their vocabulary by understanding word components and relationships between concepts.
In conclusion, decoding text is a multifaceted process that involves a range of strategies, from phonics-based decoding and context clues to sight word recognition, morphemic analysis, and semantic mapping. By understanding and applying these strategies, readers can significantly enhance their ability to decode and comprehend texts, leading to improved reading fluency and vocabulary. Whether through educational instruction or self-directed practice, developing these decoding skills is essential for anyone seeking to improve their reading abilities and engage more effectively with written communication.