The concept of equivalence point is a fundamental principle in chemistry, particularly in the context of acid-base titration. It refers to the point at which the amount of acid (or base) in a solution is exactly equal to the amount required to react with a given amount of base (or acid). This concept is crucial in understanding various chemical reactions and processes. In this article, we will delve into the five ways equivalence point works, exploring its significance and applications in different fields.
Key Points
- The equivalence point is the point at which the amount of acid or base in a solution is exactly equal to the amount required to react with a given amount of base or acid.
- It is determined by the stoichiometry of the reaction and is typically indicated by a color change or other visual indicator.
- The equivalence point is crucial in acid-base titration, where it is used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base.
- It also plays a significant role in buffer solutions, where it helps to maintain a stable pH.
- In addition, the equivalence point is important in industrial processes, such as wastewater treatment and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Understanding Equivalence Point
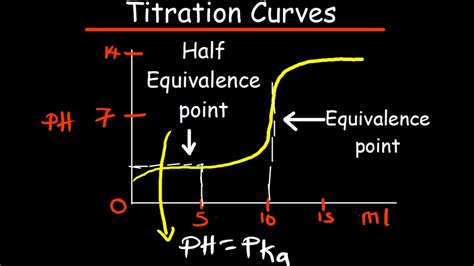
The equivalence point is a critical concept in chemistry, and its understanding is essential for various applications. It is the point at which the reaction between an acid and a base is complete, and the resulting solution is neutral. This point is often indicated by a color change or other visual indicator, such as a pH indicator. The equivalence point is determined by the stoichiometry of the reaction, which is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products.
Stoichiometry and Equivalence Point
The stoichiometry of a reaction is crucial in determining the equivalence point. It is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products, and it is expressed in terms of moles. The stoichiometry of a reaction can be represented by a balanced chemical equation, which shows the ratio of reactants to products. For example, the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) can be represented by the following equation: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O. From this equation, we can see that one mole of HCl reacts with one mole of NaOH to produce one mole of NaCl and one mole of H2O.
| Reactant | Product |
|---|---|
| 1 mole HCl | 1 mole NaCl |
| 1 mole NaOH | 1 mole H2O |
Applications of Equivalence Point
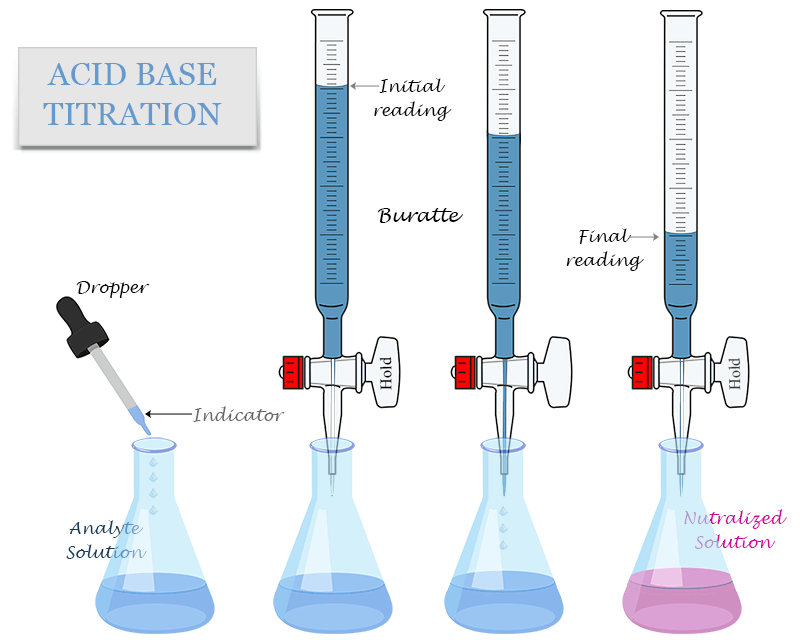
The equivalence point has numerous applications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and industry. One of the most significant applications is in acid-base titration, where it is used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. The equivalence point is also crucial in buffer solutions, where it helps to maintain a stable pH. In addition, the equivalence point plays a significant role in industrial processes, such as wastewater treatment and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Acid-Base Titration and Equivalence Point
Acid-base titration is a laboratory technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. The equivalence point is crucial in this technique, as it indicates the point at which the reaction between the acid and base is complete. The equivalence point is typically indicated by a color change or other visual indicator, such as a pH indicator. The concentration of the unknown acid or base can then be calculated using the stoichiometry of the reaction and the volume of the titrant required to reach the equivalence point.
What is the significance of the equivalence point in acid-base titration?
+The equivalence point is significant in acid-base titration because it indicates the point at which the reaction between the acid and base is complete. It allows us to calculate the concentration of the unknown acid or base using the stoichiometry of the reaction and the volume of the titrant required to reach the equivalence point.
How is the equivalence point determined in a titration reaction?
+The equivalence point is determined by the stoichiometry of the reaction and is typically indicated by a color change or other visual indicator, such as a pH indicator.
What are the applications of the equivalence point in industrial processes?
+The equivalence point has numerous applications in industrial processes, including wastewater treatment and pharmaceutical manufacturing. It is used to determine the concentration of acids and bases, and to maintain a stable pH in buffer solutions.
In conclusion, the equivalence point is a critical concept in chemistry, and its understanding is essential for various applications. It is the point at which the reaction between an acid and a base is complete, and the resulting solution is neutral. The equivalence point is determined by the stoichiometry of the reaction, which is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products. Its applications are numerous, including acid-base titration, buffer solutions, and industrial processes. By understanding the equivalence point, we can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of chemical reactions, and apply this knowledge to solve real-world problems.



