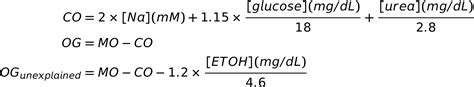The osmolal gap is a calculated measure that helps clinicians diagnose and manage various conditions, particularly those related to toxic ingestions, metabolic disorders, and renal diseases. It is defined as the difference between the measured osmolality and the calculated osmolality of serum. Measured osmolality is determined by laboratory tests, while calculated osmolality is derived from the concentrations of sodium, glucose, and urea in the blood. The osmolal gap calculator tool is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals, as it provides a quick and accurate way to calculate this critical parameter.
Understanding the Osmolal Gap

The osmolal gap is an important indicator of the presence of osmotically active substances in the blood that are not accounted for by the usual constituents, such as sodium, glucose, and urea. A normal osmolal gap typically ranges from -10 to 10 mOsm/kg, though this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific methods used for measurement. An increased osmolal gap suggests the presence of an unmeasured solute, which could be due to a variety of causes including toxic ingestions (e.g., methanol, ethylene glycol), ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, and certain renal disorders.
Calculation of the Osmolal Gap
The calculation of the osmolal gap involves measuring the serum osmolality directly using an osmometer and calculating it indirectly from the concentrations of sodium, glucose, and urea. The formula for the calculated osmolality is: 2 x (sodium) + glucose/18 + BUN/2.8, where sodium is measured in mmol/L, glucose in mg/dL, and BUN (blood urea nitrogen) in mg/dL. The osmolal gap is then determined by subtracting the calculated osmolality from the measured osmolality.
| Component | Unit of Measurement | Formula Component |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium | mmol/L | 2 x Sodium |
| Glucose | mg/dL | Glucose / 18 |
| BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) | mg/dL | BUN / 2.8 |

Using the Osmolar Gap Calculator Tool

The osmolal gap calculator tool simplifies the process of calculating the osmolal gap by automating the formula and allowing for quick input of laboratory values. These tools are often available online or as part of medical software and can significantly reduce the time and potential for error in calculating this critical parameter. When using such a tool, it is essential to ensure that the input values are accurate and to consider the clinical context in which the osmolal gap is being interpreted.
Clinical Interpretation and Management
The clinical interpretation of the osmolal gap involves considering the patient’s overall clinical presentation, including symptoms, other laboratory findings, and potential exposures to toxins. An elevated osmolal gap can prompt further diagnostic testing, such as specific toxicology screens, and guide therapeutic interventions, including the administration of antidotes or supportive care for managing the underlying condition. It is also important to monitor the osmolal gap over time to assess the effectiveness of treatment and to adjust the management plan as necessary.
Key Points
- The osmolal gap is a critical parameter in diagnosing and managing conditions related to toxic ingestions and metabolic disorders.
- It is calculated by subtracting the calculated osmolality from the measured osmolality of serum.
- A normal osmolal gap ranges from -10 to 10 mOsm/kg, though this can vary slightly by laboratory.
- An elevated osmolal gap suggests the presence of an unmeasured solute and can prompt further diagnostic testing and specific therapeutic interventions.
- Clinical interpretation of the osmolal gap requires consideration of the patient's overall clinical presentation and other laboratory findings.
In conclusion, the osmolal gap calculator tool is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals, providing a quick and accurate way to calculate this important parameter. Understanding the concept of the osmolal gap, its calculation, and its clinical interpretation is essential for diagnosing and managing a range of critical conditions effectively.
What is the normal range for the osmolal gap?
+The normal range for the osmolal gap typically ranges from -10 to 10 mOsm/kg, though this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific methods used for measurement.
What does an elevated osmolal gap indicate?
+An elevated osmolal gap suggests the presence of an unmeasured solute in the blood, which could be due to a variety of causes including toxic ingestions, ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, and certain renal disorders.
How is the osmolal gap calculated?
+The osmolal gap is calculated by subtracting the calculated osmolality from the measured osmolality of serum. Calculated osmolality is derived from the concentrations of sodium, glucose, and urea in the blood using the formula: 2 x (sodium) + glucose/18 + BUN/2.8.