Spanish is a rich and expressive language, and mastering its various verb tenses is essential for effective communication. One of the most useful and versatile tenses in Spanish is the present progressive, which is used to describe actions that are currently in progress. In this article, we will delve into the world of Spanish present progressive, exploring its structure, usage, and providing 5 valuable tips to help you improve your command of this essential tense.
Key Points
- The Spanish present progressive tense is formed using the present tense of the verb "estar" and the gerund of the main verb.
- The present progressive is used to describe actions that are currently happening, temporary actions, and actions that are happening at the moment of speaking.
- It is essential to understand the difference between the present simple and present progressive tenses to use them correctly.
- Practice is key to mastering the present progressive tense, and using it in context will help you develop a deeper understanding of its usage.
- Listening to and imitating native speakers can help you improve your pronunciation and intonation when using the present progressive tense.
Understanding the Spanish Present Progressive

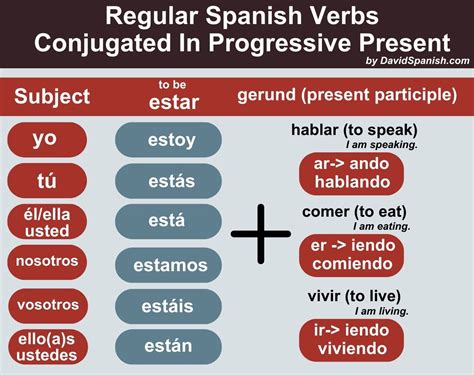
The Spanish present progressive tense is a compound tense that consists of two parts: the present tense of the verb “estar” (to be) and the gerund of the main verb. The gerund is formed by adding the suffix “-ando” or “-iendo” to the stem of the verb, depending on its conjugation. For example, the verb “hablar” (to speak) becomes “hablando” in the gerund form, while the verb “vivir” (to live) becomes “viviendo”.
Forming the Present Progressive
To form the present progressive, you need to conjugate the verb “estar” in the present tense and then add the gerund of the main verb. The conjugation of “estar” in the present tense is as follows: yo estoy, tú estás, él/ella/usted está, nosotros/as estamos, vosotros/as estáis, ellos/as están. For example, “yo estoy hablando” (I am speaking), “tú estás estudiando” (you are studying), and “ellos están trabajando” (they are working).
| Subject | Conjugation of Estar | Gerund of Main Verb | Present Progressive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo | estoy | hablando | yo estoy hablando |
| Tú | estás | estudiando | tú estás estudiando |
| Él/Ella/Usted | está | trabajando | él/ella/usted está trabajando |
5 Tips for Mastering the Spanish Present Progressive
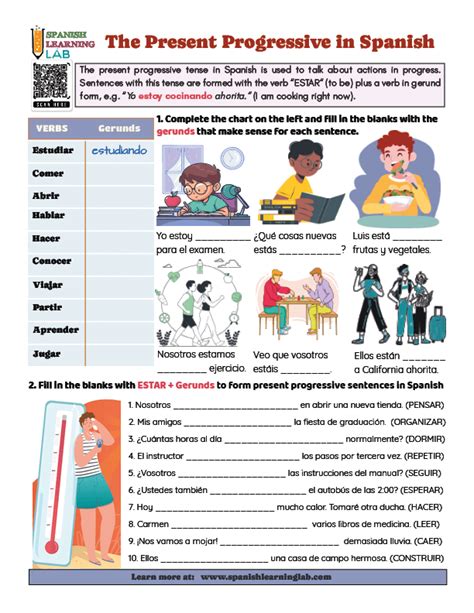
Now that we have explored the structure and usage of the Spanish present progressive, let’s dive into 5 valuable tips to help you improve your command of this essential tense.
Tip 1: Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice is key to mastering any language skill, and the present progressive is no exception. Try to use the present progressive in context as much as possible, either by speaking with native speakers, writing journal entries, or even thinking in Spanish. The more you practice, the more natural it will become.
Tip 2: Listen to Native Speakers
Listening to native speakers is an excellent way to improve your pronunciation and intonation when using the present progressive. Pay attention to how they form the tense, the emphasis they place on certain words, and the rhythm of their speech. You can find numerous resources online, such as podcasts, videos, and language exchange websites.
Tip 3: Focus on the Difference between Present Simple and Present Progressive
Understanding the difference between the present simple and present progressive tenses is crucial for using them correctly. The present simple is used to describe habitual or routine actions, while the present progressive is used to describe actions that are currently in progress. For example, “yo como una manzana todos los días” (I eat an apple every day) vs. “yo estoy comiendo una manzana ahora” (I am eating an apple now).
Tip 4: Use the Present Progressive to Describe Temporary Actions
The present progressive can also be used to describe temporary actions or actions that are happening at the moment of speaking. For example, “yo estoy visitando a mi familia por un par de semanas” (I am visiting my family for a couple of weeks). This usage is essential for describing situations that are not permanent or routine.
Tip 5: Pay Attention to the Gerund Form
Finally, it’s essential to pay attention to the gerund form of the verb when using the present progressive. The gerund form can change depending on the verb conjugation, so make sure to practice the different forms to become more comfortable with them. For example, the verb “poder” (to be able to) becomes “pudiendo” in the gerund form, while the verb “decir” (to say) becomes “diciendo”.
What is the main difference between the present simple and present progressive tenses in Spanish?
+The main difference between the present simple and present progressive tenses is that the present simple is used to describe habitual or routine actions, while the present progressive is used to describe actions that are currently in progress.
How do I form the present progressive tense in Spanish?
+To form the present progressive tense, you need to conjugate the verb "estar" in the present tense and then add the gerund of the main verb. For example, "yo estoy hablando" (I am speaking), "tú estás estudiando" (you are studying), and "ellos están trabajando" (they are working).
What are some common uses of the present progressive tense in Spanish?
+The present progressive tense is commonly used to describe actions that are currently in progress, temporary actions, and actions that are happening at the moment of speaking. For example, "yo estoy comiendo una manzana ahora" (I am eating an apple now), "yo estoy visitando a mi familia por un par de semanas" (I am visiting my family for a couple of weeks), and "ellos están trabajando en un proyecto importante" (they are working on an important project).
In conclusion, mastering the Spanish present progressive tense is essential for effective communication in Spanish. By following these 5 tips and practicing regularly, you can improve your command of this versatile tense and become a more confident and proficient Spanish speaker.