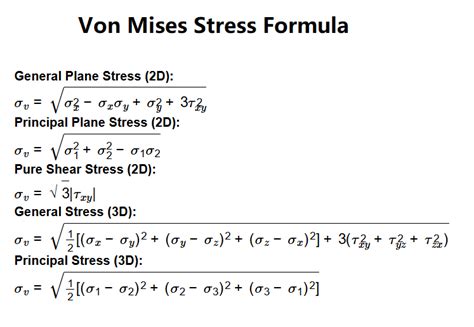
The Von Mises stress equation is a fundamental concept in the field of mechanics of materials, playing a crucial role in understanding the behavior of materials under various types of loading. It is named after Richard von Mises, who first proposed it in the early 20th century. This equation is used to predict the failure of ductile materials, which are materials that can undergo significant plastic deformation before failing. The Von Mises stress, often denoted as σ_v, is a measure of the overall stress state in a material and is particularly useful for assessing the likelihood of yielding, which is the onset of plastic deformation.
Key Points
- The Von Mises stress equation combines the effects of normal and shear stresses to predict material failure.
- It is widely used in engineering design to ensure that components can withstand the stresses they will experience in service.
- The equation is based on the idea that failure occurs when the distortion energy per unit volume reaches a critical value.
- Von Mises stress is particularly useful for analyzing the behavior of ductile materials under complex loading conditions.
- It provides a single value that can be compared to the yield strength of the material to determine if yielding will occur.
Mathematical Formulation
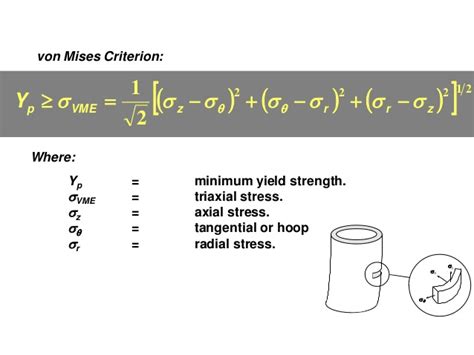
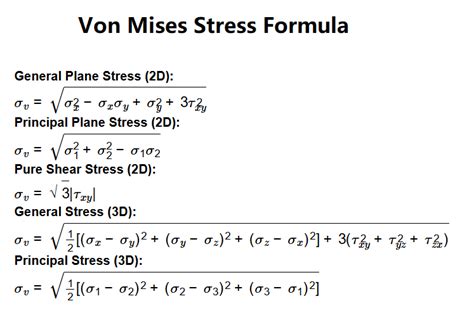
The Von Mises stress (σ_v) can be calculated using the principal stresses (σ_1, σ_2, σ_3) of a material. The equation is as follows:
σ_v = √[(σ_1 - σ_2)^2 + (σ_2 - σ_3)^2 + (σ_3 - σ_1)^2] / 2
This equation shows that the Von Mises stress depends on the differences between the principal stresses, reflecting the distortional energy in the material. For situations where the stress state is simpler, such as uniaxial tension or compression, the Von Mises stress simplifies to the applied stress, since the other principal stresses are zero.
Understanding Principal Stresses
Principal stresses are the normal stresses acting on the principal planes of a material, where the shear stresses are zero. They are determined by transforming the stress tensor to find the orientation of these planes and the magnitude of the stresses acting on them. The principal stresses are important because they represent the maximum and minimum normal stresses in the material, which are critical for understanding the material’s response to loading.
| Stress Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Normal Stress | Stress perpendicular to the surface of a material |
| Shear Stress | Stress parallel to the surface of a material |
| Principal Stress | Normal stress acting on a principal plane |

Applications and Limitations
The Von Mises stress equation is widely applied in engineering to assess the integrity of structures and components under complex loading conditions. It is particularly useful for designing against yielding in ductile materials, such as metals. However, it has limitations, including not accounting for the effects of hydrostatic stress on the failure of brittle materials, which can fail under tensile stress even if the Von Mises stress is below the yield strength. Additionally, it does not account for factors like fatigue, creep, or corrosion, which can also lead to material failure.
Material Failure Theories
Several material failure theories exist, each applicable to different types of materials and loading conditions. The Tresca criterion, for example, predicts failure based on the maximum shear stress in the material, and is simpler to apply than the Von Mises criterion but less accurate for many materials. The Mohr-Coulomb theory is used for brittle materials and incorporates both normal and shear stresses to predict failure. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each theory is crucial for selecting the appropriate method for analyzing material behavior.
Meta description suggestion: "Understand the Von Mises stress equation and its application in predicting material failure, particularly for ductile materials under complex loading conditions."
What is the primary use of the Von Mises stress equation?
+The primary use of the Von Mises stress equation is to predict the onset of yielding in ductile materials under complex loading conditions, allowing engineers to design components that can withstand the stresses they will experience in service.
How does the Von Mises stress equation account for different types of stress?
+The Von Mises stress equation combines the effects of normal and shear stresses by considering the differences between the principal stresses, providing a comprehensive measure of the stress state in a material.
What are the limitations of the Von Mises stress equation?
+The Von Mises stress equation does not account for the effects of hydrostatic stress on brittle materials, nor does it consider factors like fatigue, creep, or corrosion. It is also less applicable to materials that exhibit significant anisotropy or to situations involving high strain rates.