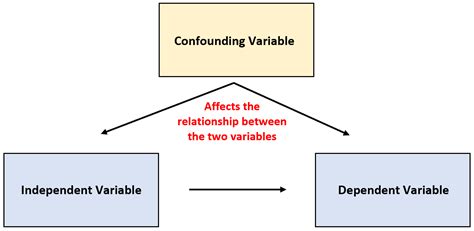
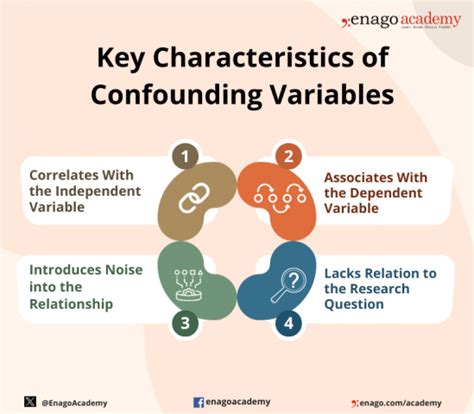
A confounding variable, also known as a confounder or confounding factor, is an external variable that can influence the relationship between the independent and dependent variables in a study, potentially leading to biased or misleading conclusions. In other words, a confounding variable is a factor that can affect the outcome of a study, making it difficult to determine whether the observed effect is due to the independent variable or the confounding variable.
Definition and Examples
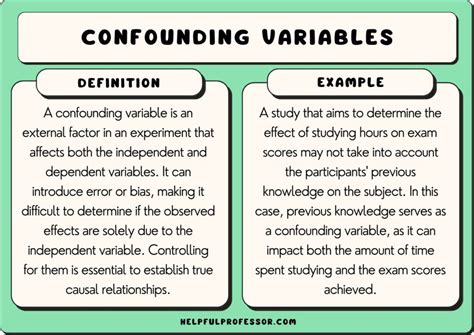
A confounding variable can be any factor that is related to both the independent and dependent variables, such as demographics, environmental factors, or pre-existing conditions. For instance, in a study examining the relationship between exercise and weight loss, a confounding variable could be diet. If participants who exercise regularly also tend to eat a healthier diet, it may be difficult to determine whether the weight loss is due to the exercise or the diet. Other examples of confounding variables include age, gender, socioeconomic status, and comorbidities.
Types of Confounding Variables
There are several types of confounding variables, including:
- Demographic confounders: Factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status that can affect the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- Environmental confounders: Factors such as pollution, climate, and access to healthcare that can influence the outcome of a study.
- Behavioral confounders: Factors such as diet, exercise, and smoking that can affect the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- Pre-existing condition confounders: Factors such as chronic diseases or disabilities that can influence the outcome of a study.
| Type of Confounder | Example |
|---|---|
| Demographic | Age, gender, ethnicity |
| Environmental | Pollution, climate, access to healthcare |
| Behavioral | Diet, exercise, smoking |
| Pre-existing condition | Chronic diseases, disabilities |
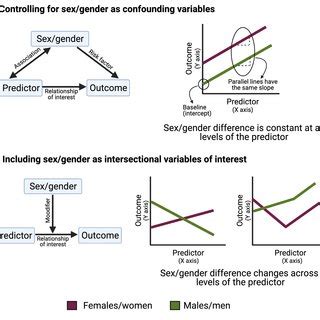
Controlling for Confounding Variables
There are several methods to control for confounding variables, including:
- Matching: Matching participants based on relevant characteristics to reduce the impact of confounding variables.
- Stratification: Dividing participants into subgroups based on relevant characteristics to control for confounding variables.
- Regression analysis: Using statistical models to control for confounding variables and estimate the effect of the independent variable.
- Instrumental variable analysis: Using an instrumental variable to control for confounding variables and estimate the causal effect of the independent variable.
Key Points
- A confounding variable is an external variable that can influence the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- Confounding variables can be demographic, environmental, behavioral, or pre-existing condition-related.
- Identifying and controlling for confounding variables is crucial in research design to ensure the validity and reliability of the results.
- Methods to control for confounding variables include matching, stratification, regression analysis, and instrumental variable analysis.
- Controlling for confounding variables can reduce bias and increase the accuracy of research findings.
Real-World Examples
Confounding variables can have significant impacts on real-world studies and decisions. For instance, a study examining the relationship between vaccination and autism risk may be confounded by factors such as age, socioeconomic status, and access to healthcare. If the study does not control for these confounding variables, the results may be misleading and lead to incorrect conclusions.
What is the difference between a confounding variable and a moderating variable?
+A confounding variable is a variable that affects the relationship between the independent and dependent variables, while a moderating variable is a variable that affects the strength or direction of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
How can researchers identify confounding variables in their study?
+Researchers can identify confounding variables by reviewing the literature, conducting pilot studies, and using statistical methods such as regression analysis to examine the relationships between variables.
What are the consequences of not controlling for confounding variables in a study?
+Not controlling for confounding variables can lead to biased or misleading results, which can have significant consequences in fields such as healthcare, policy-making, and business.
In conclusion, confounding variables are external factors that can influence the relationship between the independent and dependent variables in a study, potentially leading to biased or misleading conclusions. By understanding the types of confounding variables, methods to control for them, and the importance of controlling for them, researchers can design and conduct studies that produce valid and reliable results.