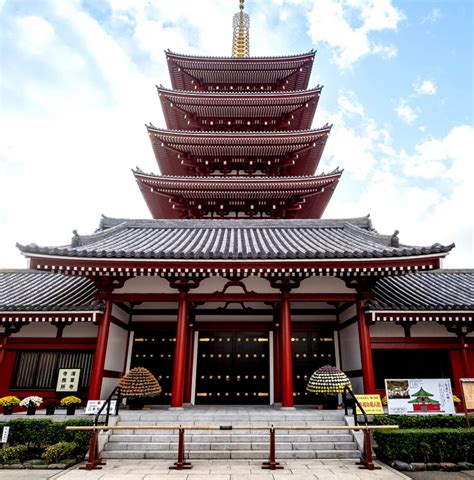
A pagoda is a type of religious building that originated in Asia, particularly in China, Japan, and Southeast Asia. The term "pagoda" is derived from the Portuguese word "pagode," which refers to a temple or a sacred building. Pagodas are typically designed to house Buddhist relics, scriptures, or statues, and they serve as a place of worship, meditation, and spiritual growth for Buddhists and other Eastern religious practitioners.
History and Evolution of Pagodas
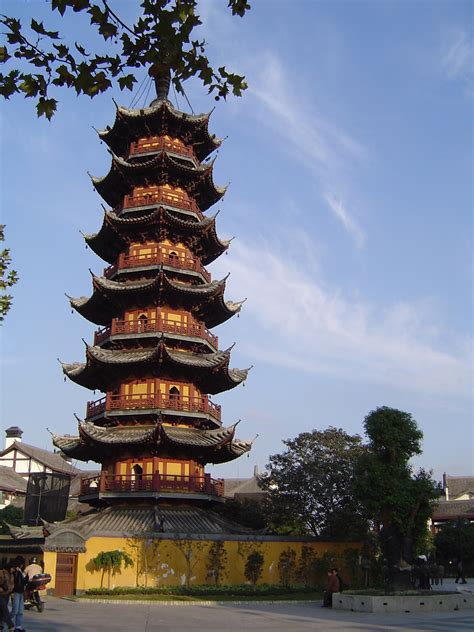

Pagodas have a rich history that dates back to the 3rd century BCE, during the reign of the Indian emperor Ashoka. The first pagodas were built in India as stupas, which were mound-like structures that housed Buddhist relics. As Buddhism spread throughout Asia, the design and architecture of pagodas evolved, incorporating local materials, styles, and cultural influences. In China, pagodas were built during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE) and became an integral part of Chinese Buddhist architecture. In Japan, pagodas were introduced during the 6th century CE and were influenced by Chinese and Korean architectural styles.
Characteristics of Pagodas
Pagodas are typically characterized by their distinctive architectural features, which include:
- A multi-tiered or multi-story structure, often with a square or rectangular base and a series of diminishing roofs
- A central pillar or axis that supports the weight of the building
- A finial or spire at the top, often adorned with decorative motifs or sculptures
- Elaborate carvings, sculptures, or paintings that depict Buddhist stories, symbols, or deities
- A peaceful and serene atmosphere, often achieved through the use of natural materials, water features, and carefully designed gardens
| Country | Notable Pagodas |
|---|---|
| China | Big Wild Goose Pagoda, Small Wild Goose Pagoda, Pagoda of the Six Harmonies |
| Japan | Kiyomizu-dera Pagoda, Todai-ji Pagoda, Five-Story Pagoda of Kiyomizu-dera |
| Thailand | Wat Arun Pagoda, Wat Phra Kaew Pagoda, Wat Traimit Pagoda |

Types of Pagodas

There are several types of pagodas, each with its unique characteristics and functions. Some of the most common types of pagodas include:
- Stupa pagodas, which are mound-like structures that house Buddhist relics
- Temple pagodas, which are larger buildings that serve as places of worship and meditation
- Tower pagodas, which are tall, slender structures that are often used as landmarks or observation towers
- Garden pagodas, which are small, ornate buildings that are situated in gardens or parks
Key Points
- Pagodas are religious buildings that originated in Asia and serve as places of worship, meditation, and spiritual growth
- Pagodas have a rich history and have evolved over time, incorporating local materials, styles, and cultural influences
- Pagodas are characterized by their distinctive architectural features, including multi-tiered structures, central pillars, and finials
- There are several types of pagodas, each with its unique characteristics and functions
- Pagodas are often adorned with elaborate carvings, sculptures, or paintings that depict Buddhist stories, symbols, or deities
Cultural Significance of Pagodas
Pagodas have played a significant role in the cultural and spiritual lives of people in Asia and beyond. They are not only places of worship and meditation but also serve as centers of learning, art, and architecture. Pagodas have been built to commemorate important events, honor revered figures, and provide a sense of community and belonging. In many Asian cultures, pagodas are considered sacred spaces that embody the principles of Buddhism, such as compassion, wisdom, and mindfulness.
Today, pagodas continue to be an important part of Asian culture and heritage, attracting millions of visitors and pilgrims each year. They serve as a reminder of the region's rich history, cultural diversity, and spiritual traditions. As a symbol of peace, harmony, and enlightenment, pagodas remain an enduring and inspiring presence in the modern world.
What is the purpose of a pagoda?
+The purpose of a pagoda is to serve as a place of worship, meditation, and spiritual growth for Buddhists and other Eastern religious practitioners. Pagodas are designed to house Buddhist relics, scriptures, or statues, and they provide a peaceful and serene atmosphere for devotees to practice their faith.
What are the different types of pagodas?
+There are several types of pagodas, including stupa pagodas, temple pagodas, tower pagodas, and garden pagodas. Each type of pagoda has its unique characteristics and functions, and they are often built to serve specific purposes or commemorate important events.
What is the cultural significance of pagodas?
+Pagodas have played a significant role in the cultural and spiritual lives of people in Asia and beyond. They are not only places of worship and meditation but also serve as centers of learning, art, and architecture. Pagodas are considered sacred spaces that embody the principles of Buddhism, such as compassion, wisdom, and mindfulness.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the history, architecture, and cultural significance of pagodas, iconic religious buildings that originated in Asia and serve as places of worship, meditation, and spiritual growth.” (149 characters)