The concept of "Y" can be understood in various contexts, depending on the field or discipline being referred to. In a broad sense, "Y" can represent a variable, a coordinate, or a symbol with specific meanings in mathematics, genetics, sociology, and other areas. To delve into the explanation of "Y," it's essential to consider the context in which it is being used.
Mathematical Context

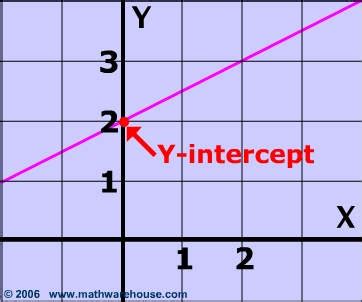
In mathematics, “Y” is often used as a variable to represent an unknown value or a coordinate in a two-dimensional or three-dimensional space. For instance, in the Cartesian coordinate system, “Y” represents the vertical axis, while “X” represents the horizontal axis. The equation of a line can be expressed as Y = mx + b, where “m” is the slope, “b” is the y-intercept, and “x” and “y” are the coordinates of any point on the line.
Genetic Context
In genetics, the “Y” chromosome plays a crucial role in determining the sex of an individual. Humans and many other species have a sex determination system where females have two “X” chromosomes (XX), and males have one “X” and one “Y” chromosome (XY). The “Y” chromosome carries genes that are essential for male development, including the SRY gene, which triggers the development of testes in the embryo.
| Chromosome | Sex Determination |
|---|---|
| XX | Female |
| XY | Male |

Sociological Context
In sociology, the term “Generation Y” refers to people born between the early 1980s and the mid-1990s, following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. This generation is characterized by growing up during a time of rapid technological change, social media saturation, and economic uncertainty. Members of Generation Y are often associated with traits such as tech-savviness, diversity, and a desire for work-life balance.
The concept of "Y" can also be related to other areas, such as psychology, where it might symbolize a specific aspect of human behavior or cognition, or in physics, where it could represent a variable in equations describing phenomena like electromagnetism or quantum mechanics.
Key Points
- The meaning of "Y" varies significantly depending on the context, including mathematical, genetic, sociological, and other disciplines.
- In mathematics, "Y" is used as a variable or coordinate, while in genetics, it refers to the chromosome responsible for male sex determination.
- Generation Y, in sociology, denotes a demographic cohort with distinct characteristics shaped by technological, social, and economic factors.
- The interpretation of "Y" requires understanding the specific field or context in which it is being discussed.
- Expert insight into the concept of "Y" highlights the complexity and multifaceted nature of this symbol across different domains.
Understanding the concept of "Y" in its various contexts requires a nuanced approach, acknowledging the distinct meanings and implications it carries across different fields of study. By recognizing these differences, individuals can better appreciate the complexity and depth of knowledge associated with the symbol "Y" and its applications.
What does "Y" represent in the context of genetics?
+In genetics, the "Y" chromosome is crucial for determining male sex and carries genes necessary for male development.
How is "Y" used in mathematical equations?
+In mathematics, "Y" is often used as a variable or to represent the vertical axis in coordinate systems, such as in the equation of a line (Y = mx + b).
What characterizes Generation Y in sociology?
+Generation Y, or Millennials, are characterized by their tech-savviness, diversity, and a desire for work-life balance, having grown up during a period of significant technological and social change.
As the concept of “Y” continues to evolve across various disciplines, understanding its multifaceted nature is essential for navigating the complexities of modern knowledge and applying insights from one field to another. The dynamic and context-dependent meaning of “Y” underscores the importance of interdisciplinary approaches and the value of nuanced, expert perspectives in unraveling the intricacies of human knowledge.



