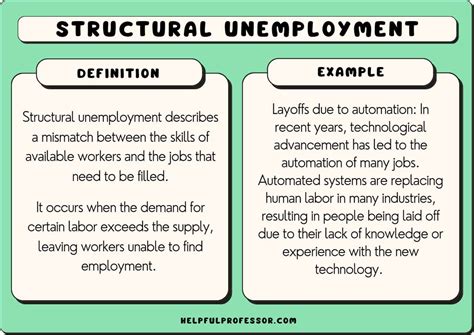
Structural unemployment is a persistent and complex issue that affects many economies around the world. It occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills and qualifications of the workforce and the requirements of available job openings. This type of unemployment is often caused by changes in technology, industry trends, and shifts in the global economy. For instance, the rise of automation and artificial intelligence has led to the displacement of workers in certain sectors, such as manufacturing and customer service. According to a report by the McKinsey Global Institute, up to 800 million jobs could be lost worldwide due to automation by 2030.
In the United States, for example, the decline of the coal mining industry has led to significant job losses in regions where coal mining was a dominant employer. The closure of coal mines and the shift towards renewable energy sources have resulted in a surplus of workers with skills that are no longer in demand. Similarly, the decline of the manufacturing sector in the Midwest has led to a mismatch between the skills of the workforce and the requirements of the available job openings. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the unemployment rate in the Midwest region was 4.3% in January 2022, higher than the national average of 4.0%.
Key Points
- Structural unemployment occurs due to a mismatch between worker skills and job requirements
- Technological changes, industry trends, and global economic shifts can cause structural unemployment
- Examples of structural unemployment include the decline of the coal mining and manufacturing sectors in the United States
- Up to 800 million jobs could be lost worldwide due to automation by 2030, according to the McKinsey Global Institute
- Addressing structural unemployment requires investment in education and training programs to upskill workers
Causes of Structural Unemployment

There are several causes of structural unemployment, including technological changes, industry trends, and shifts in the global economy. Technological advancements, such as automation and artificial intelligence, have increased productivity and efficiency but have also displaced workers in certain sectors. Industry trends, such as the decline of the manufacturing sector, have led to a mismatch between the skills of the workforce and the requirements of the available job openings. Shifts in the global economy, such as the rise of emerging markets, have also led to changes in the demand for certain skills and qualifications.
Technological Unemployment
Technological unemployment occurs when technological advancements, such as automation and artificial intelligence, displace workers in certain sectors. This type of unemployment is often caused by the increased use of machines and computers, which can perform tasks more efficiently and accurately than humans. According to a report by the Brookings Institution, nearly 40% of jobs in the United States are at high risk of being automated, with the majority of these jobs being in the service sector.
| Industry | Percentage of Jobs at High Risk of Automation |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 70% |
| Transportation and Warehousing | 63% |
| Customer Service | 55% |
| Food Preparation and Service | 52% |
Solutions to Structural Unemployment

Addressing structural unemployment requires a multifaceted approach that involves government policies, education and training programs, and industry initiatives. Governments can implement policies that support workers who have lost their jobs due to technological changes or industry trends, such as providing unemployment benefits and job training programs. Education and training programs can help workers develop new skills and qualifications that are in demand, while industry initiatives can provide workers with opportunities to upskill and reskill.
Education and Training Programs
Education and training programs are essential for addressing structural unemployment. These programs can help workers develop new skills and qualifications that are in demand, such as data science, cybersecurity, and healthcare. According to a report by the World Economic Forum, by 2022, more than a third of the desired skills for most jobs will be comprised of skills that are not yet considered crucial to the job today. Investing in education and training programs can help workers develop these skills and increase their employability.
In conclusion, structural unemployment is a complex issue that requires a comprehensive approach to address. By understanding the causes of structural unemployment, including technological changes, industry trends, and shifts in the global economy, we can develop effective solutions to address this issue. Investing in education and training programs, implementing policies that support workers, and providing industry initiatives can help workers develop new skills and qualifications, increase their employability, and reduce the risk of structural unemployment.
What is structural unemployment?
+Structural unemployment occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills and qualifications of the workforce and the requirements of available job openings.
What causes structural unemployment?
+Structural unemployment is caused by technological changes, industry trends, and shifts in the global economy.
How can structural unemployment be addressed?
+Addressing structural unemployment requires a multifaceted approach that involves government policies, education and training programs, and industry initiatives.